Securing Global Supply Chains: ISO 28000, ISO 22301 & Beyond

In today's interconnected world, securing global supply chains is more important than ever. There are constantly more risks related to natural disasters, cyber threats, geopolitical instability, and various disruptions cause by events such as the recent COVID-19 pandemic
ISO 28000, ISO 22301, CTPAT (Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism), and related frameworks have provided organizations with the ability to manage relevant risks and enable business continuity as well improve security and safety for the organization and supply chains.
In this blog post, we will see how ISO certifications including ISO 28000 and ISO 22301 secure an organization's supply chain and optimize them too.
For assistance, contact us at [email protected].
Introduction
With globalization continuing to increase the complexity of supply chains, organizations are under increasing pressure to keep them secure, resilient, and in compliance with international and domestic regulations. Securing global supply chains is critical for safeguarding physical assets and information, sustaining customer confidence, maintaining financial performance, and complying with trade compliance.
ISO 28000, ISO 22301, and other security frameworks enable organizations to manage supply chain security risks by providing a roadmap to increase resilience, reduce vulnerabilities, and enable continuity of an organization’s objectives when supply chains are threatened.
ISO 28000 Certification Process for Logistics Operators
ISO 28000 is a global standard for supply chain security management to ensure the protection of goods and materials from origin to the delivered point. The process ISO 28000 certification has key basic steps:
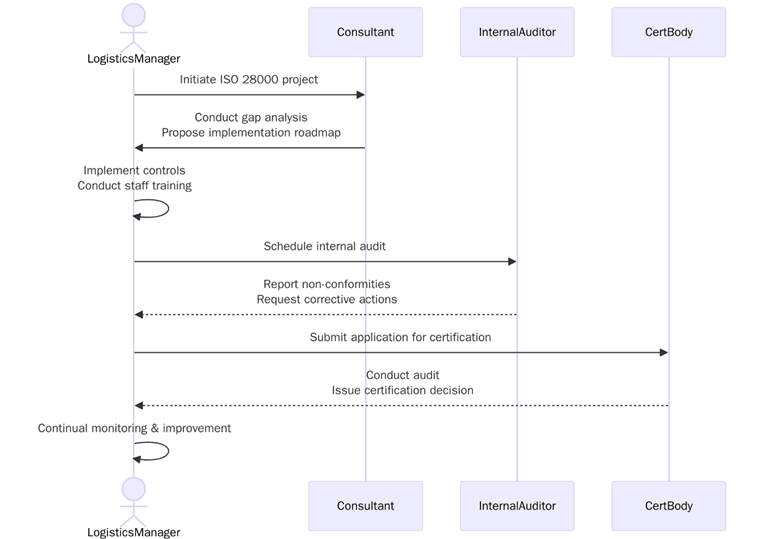
- Risk Assessment and Identification: The first step of the process is risk assessment, which will allow the organization to identify potential threats, vulnerabilities and uses disruption in its supply chain activity.
- Implementation of Security Controls: Based on the risk assessment identified and threats, the organization will take action and implement appropriate security controls.
- Documentation and Reporting: The organization will need to document its security policies, processes, and procedures to both demonstrate compliance with the ISO 28000 requirements as well as provide visibility and accountability up and down the supply chain.
- Audit and Certification: An accredited certification body will perform an audit to assess if the organizations supply chain security management system complies with the ISO 28000 standards.
ISO 28001 vs CTPAT: Choosing the Right Framework
ISO 28001 and CTPAT are both prominent frameworks for securing supply chains, each with distinct benefits. While both frameworks aim to upgrade security, they differ in their approach and application.
Aspect | ISO 28001 | CTPAT (Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism) | |
Scope | Global standard for supply chain security management | U.S.-specific initiative for securing international trade with the U.S. | |
Focus | Comprehensive approach to supply chain security including risk management and physical security | Focused on securing supply chains involved in U.S. imports and exports | |
Target Audience | Applicable to any organization with a supply chain security concern | Primarily U.S. importers and exporters | |
Regulatory Alignment | Aligns with international security standards | Tailored to U.S. regulations, primarily concerned with reducing security risks at U.S. borders | |
Compliance Requirements | Voluntary certification for global security management | Voluntary but offers U.S. government benefits such as reduced inspections and expedited clearance | |
Emphasis | Risk management, securing goods in transit, and logistics security | Focuses on the security of cargo entering the U.S. from overseas | |
International Recognition | Globally recognized certification for supply chain security | Recognized primarily within the U.S. and its trade partners | |
Security Measures | Covers physical security, personnel, IT systems, and more | Focuses on physical security, access controls, and customs procedures | |
Benefits | Upgraded global supply chain security, reduces risks, boosts operational resilience | Provides U.S. import benefits, faster clearance, and reduced inspection frequency for certified partners |
Integrating ISO 22301 Business Continuity with Supply Chain Risk
ISO 22301 establishes a framework for developing, implementing, and maintaining a business continuity management system (BCMS). Integrating ISO 22301 with supply chain risk management enables organizations to maintain operational capacity through disruptions.
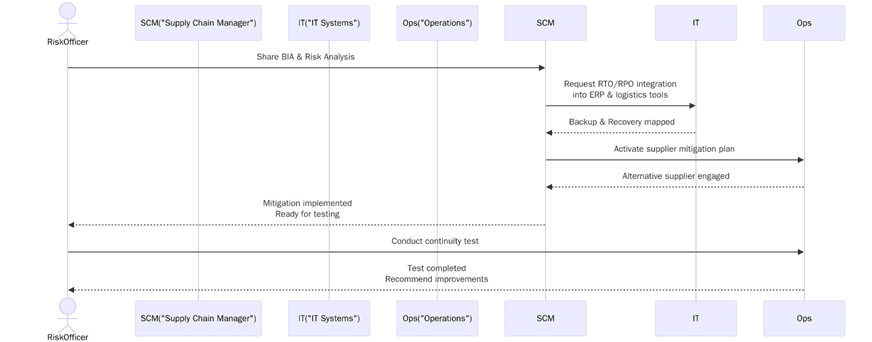
By integrating ISO 22301 with ISO 28000, organizations can develop a holistic approach to risk management that includes both security and operational continuity in the same framework or structure.
Business Continuity Planning means Developing and implementing plans to continue essential operations during disruptions. Crisis management is establishing teams that can mobilize and execute their plans efficiently during incidents that effect supply chain performance. Communication Protocols refers to establishing processes and protocol for open and honest communication with all stakeholder, suppliers, and customers during a crisis. Recovery Planning means establishing clear procedures to restore operations, minimize downtime, and reduce losses effectively.
By integrating ISO 22301 with supply chain security management, businesses ensure that they are prepared for both physical and operational disruptions. For assistance, contact us at [email protected].
Supplier Risk Assessment Using ISO 31000 Principles
ISO 31000 provides guidance on risk management and is particularly valuable for evaluating and managing supply chain risk. ISO 31000 can help evaluate these plans with its principles.
Provider risk assessment key aspects of ISO 31000 principles are:
- Risk Identification: Identifying risks in the supply chain, for example: financial problems, geopolitical risks or risks from capacity or problems at supplier.
- Risk Evaluation: Evaluate the likelihood and the effects on the business of risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Identify ways to mitigate identified risks, e.g., reducing the number of suppliers or diversifying, preparing contingency plans and increasing collaboration with key suppliers.
Case Study: Automotive Tier‑1 Supplier Achieves ISO 28000
A major Tier-1 automotive manufacturer has recently received ISO 28000 certification with the goal of improving supply chain security for its business of providing parts to global automotive manufacturers.
By working to adopt ISO 28000, the supplier was able to:
Work towards better tracking of goods moving from suppliers to customers, ultimately producing more transparency and security in the delivery of goods. Identify security risks such as theft, counterfeiting, and tampering and address them and/or upgrade controls through improved monitoring systems in place. Increasing Customer trust by demonstrating adherence to ISO 28000 certification practices and regulations to improve global supply chain security. The company could also leverage this commitment towards a review of its relationships with automotive manufacturers and customers.
Blockchain Traceability Under ISO 28000
Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool for improving traceability and transparency in supply chains. Under ISO 28000, organizations can leverage blockchain to track the movement of goods.
By integrating blockchain with ISO 28000 certification, businesses can:
- Blockchain provides an immutable record of transactions, allowing all stakeholders to access real-time information on product movement and security status.
- Blockchain technology ensures the authenticity of products by verifying each step in the supply chain, reducing the risk of counterfeit goods.
- With blockchain, organizations can securely share information across the supply chain without the risk of data manipulation or unauthorized access.
Contact Us
Pacific Certifications can assist your organization in navigating the ISO 28000 certification process. Our team of experts will guide you through the steps of implementing security measures, enhancing supply chain resilience, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
For assistance, contact us at [email protected].
Visit our website at www.pacificcert.com.
FAQs
Q1: What is ISO 28000?
ISO 28000 is an international standard for supply chain security management that provides guidelines for organizations to secure their supply chains against risks such as theft, tampering, and other disruptions.
Q2: How does ISO 28000 help logistics operators?
ISO 28000 certification helps logistics operators identify security risks, implement controls to mitigate those risks, and demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive goods throughout the supply chain.
Q3: How is ISO 28001 different from CTPAT?
ISO 28001 is a global standard for supply chain security, while CTPAT is a U.S.-based initiative focusing on supply chain security for businesses involved in international trade with the U.S. Both frameworks aim to upgrade security, but ISO 28001 provides a broader, international perspective.
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs

