ISO Certifications for Herb and Spice Processing Businesses, Requirements and Benefits

ISO Standards for Herb and Spice Processing
The global demand for herbs and spices has surged significantly, driven by consumer preference for natural flavors and health-conscious choices. However, ensuring the safety and consistency of these products is critical. This is where ISO certifications for herb and spice processing come into play.
ISO develops internationally recognized standards that help businesses maintain food safety and quality management. Adopting these standards enables herb and spice processors to meet regulatory requirements and expand into global markets.

Ensure food safety and compliance with internationally recognized ISO certifications. Get your certification process started today! Email: [email protected] | Phone: +91-8595603096.
Applicable ISO Standards for Herb and Spice Processing
The herb and spice industry must comply with various ISO standards to ensure safety and environmental sustainability. Some of the most applicable ISO certifications include:
ISO 22000: Food Safety Management System
ISO 22000 ensures that food processors, including those in the herb and spice sector, implement a comprehensive food safety management system. It integrates principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), helping businesses identify and mitigate food safety risks.
ISO 9001: Quality Management System
This standard emphasizes consistent product quality, customer satisfaction, and continual improvement. Herb and spice processors certified under ISO 9001 ensure that their products meet regulatory and customer expectations.
ISO 14001: Environmental Management System
For businesses prioritizing sustainability, ISO 14001 helps reduce environmental impact by optimizing waste management, energy consumption, and resource utilization in spice processing plants.
ISO 17025: Testing and Calibration Laboratories
Laboratories testing herb and spice samples for contaminants, microbiological hazards, and authenticity benefit from ISO 17025 certification. It ensures the accuracy and reliability of test results.
ISO 31000: Risk Management
ISO 31000 helps businesses in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with contamination, supply chain disruptions, and regulatory compliance in spice processing.
ISO 45001: Occupational Health & Safety Management System
This standard ensures worker safety in herb and spice processing plants by addressing risks related to equipment handling, exposure to chemical substances, and ergonomic concerns.
ISO 22005: Traceability in the Food Chain
ISO 22005 certification is crucial for ensuring the traceability of ingredients, helping processors track their supply chain and avoid fraudulent substitutions.
By implementing these ISO standards, herb and spice processors can achieve compliance, enhance market credibility, and ensure consumer safety.
Click here to find out more applicable standards to your industry
Pacific Certifications is a trusted ISO certification body that provides audit and certification services for businesses in the herb and spice processing industry. With an expert team of auditors, Pacific Certifications ensures that companies comply with ISO standards effectively.
As a third-party certification body, Pacific Certifications does not provide consultancy, gap analysis, training, or implementation services. However, businesses looking to achieve ISO 22000, ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and other relevant certifications can rely on Pacific Certifications for rigorous auditing and certification issuance.
Stand out in the market with ISO 22000, ISO 9001, and more. Our expert auditors ensure a smooth certification process. Contact us now! Write to us at: [email protected].
Requirements of ISO Certifications for Herb and Spice Processing
Each ISO standard has specific requirements that herb and spice processors must follow. Below is a summary of key requirements for each relevant ISO certification:
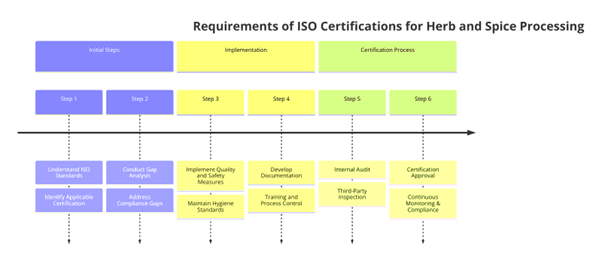
ISO 22000: Food Safety Management System (FSMS)
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) – Identify and control food safety hazards.
- Food Safety Policy – Establish documented policies for food safety management.
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) – Implement hygiene, sanitation, and process controls.
- Risk Management – Conduct food safety risk assessments and implement preventive measures.
- Traceability & Recall Procedures – Maintain records for ingredient sourcing and establish recall plans.
- Regular Audits & Continuous Improvement – Conduct internal audits and ensure compliance with food safety standards.
ISO 9001: Quality Management System (QMS)
- Customer Focus – Ensure consistent quality to meet customer requirements.
- Process Standardization – Develop and document all key processes.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions – Address non-conformities and implement improvements.
- Employee Training – Ensure workforce competency in quality control measures.
- Performance Monitoring – Track and analyze operational data for continuous improvement.
ISO 14001: Environmental Management System (EMS)
- Environmental Policy – Develop a policy to reduce environmental impact.
- Waste Management – Minimize waste and ensure proper disposal.
- Energy & Resource Efficiency – Optimize water and energy usage.
- Compliance with Legal Requirements – Meet environmental regulations and standards.
- Emergency Preparedness – Establish response plans for environmental incidents.
ISO 17025: Testing & Calibration Laboratories
- Laboratory Competency – Ensure accurate and reliable test results.
- Method Validation – Use verified and scientifically proven testing methods.
- Calibration & Equipment Maintenance – Maintain and calibrate testing equipment regularly.
- Personnel Qualifications – Train laboratory staff to meet competency requirements.
- Quality Control Procedures – Implement standardized quality control checks.
ISO 31000: Risk Management
- Risk Identification – Assess and document potential threats to food safety.
- Risk Analysis & Evaluation – Determine the impact of identified risks.
- Implementation of Risk Controls – Develop preventive and corrective measures.
- Continuous Monitoring & Review – Regularly update risk assessments and mitigation plans.
ISO 45001: Occupational Health & Safety (OHSMS)
- Workplace Safety Policy – Develop health and safety guidelines.
- Hazard Identification & Risk Control – Identify potential workplace hazards.
- Employee Training – Conduct training on safety procedures.
- Incident Reporting & Investigation – Maintain records of workplace injuries and take corrective actions.
- Emergency Preparedness & Response – Implement emergency protocols and drills.
ISO 22005: Traceability in the Food Chain
- Supply Chain Documentation – Record ingredient origins and suppliers.
- Batch Tracking System – Implement systems to trace raw materials to finished products.
- Recall & Crisis Management – Establish recall procedures for food safety incidents.
- Data Management & Storage – Maintain proper documentation for traceability compliance.
By meeting these ISO certification requirements, herb and spice processing companies can ensure product safety, quality consistency and global market compliance.
ISO certification is crucial for quality and compliance in herb & spice processing. Get certified today with Pacific Certifications! Drop us a mail: [email protected].
Benefits of ISO Certifications for Herb and Spice Processing
Compliance
ISO certification enables businesses to meet global food safety regulations, making it easier to export herbs and spices to international markets.
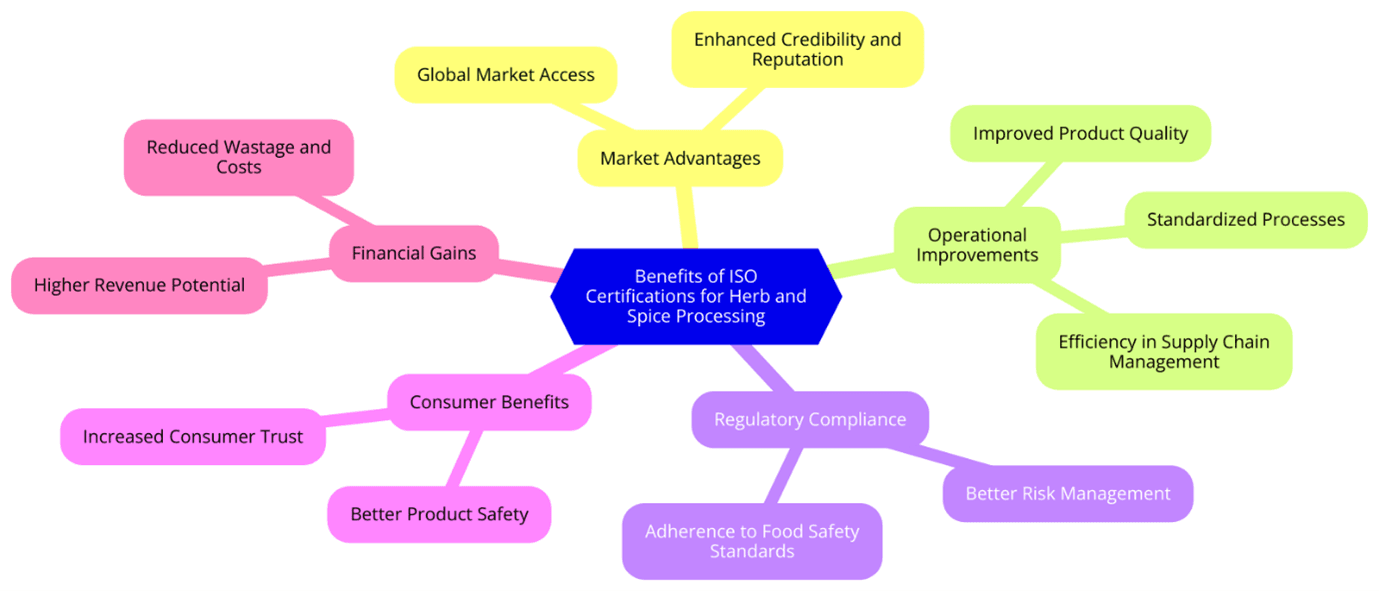
Consumer Trust
Certified businesses can display ISO certification on their products, assuring customers of their commitment to quality and safety.
Efficiency
ISO standards encourage streamlined processes, reducing waste, optimizing production, and improving overall operational efficiency.
Risk Mitigation
Through HACCP-based risk management, ISO-certified businesses can prevent contamination, adulteration, and product recalls.
Marketing Advantage
ISO certification differentiates businesses from competitors, increasing credibility in the market.
Sustainability
ISO 14001-certified businesses minimize their environmental impact through responsible resource consumption and waste management.
The global herb and spice market is projected to grow at CAGR of 5.1% this year, driven by increasing demand for organic and sustainable spices. Companies that adopt ISO certifications gain a marketing edge, especially with increasing regulatory scrutiny on food safety and traceability.
A recent study highlighted that ISO 22000-certified companies experienced 30% fewer food safety incidents, reinforcing the importance of compliance in maintaining global supply chain integrity.
Achieve ISO certification and enhance your herb and spice processing business with Pacific Certifications. Our expert auditors help you navigate the certification process efficiently!
Pacific Certifications is accredited by ABIS, in case you need support with ISO certification for your Herb and Spice Processing business, please contact us at [email protected] or +91-8595603096.
Read more at : Pacific Blogs
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs

