ISO Certifications in Pharma and Life Sciences: Regulatory & Quality Alignment

Pharma and life sciences work under close scrutiny from regulators, patients and partners. From research to manufacturing and supply, every step must protect patient safety, product quality and data integrity. Institutions face inspections, supplier audits and complex partner networks while managing sensitive data and global cold chains. ISO certifications give a clear, internationally recognized way to run these operations with discipline that aligns with Goods practice expectations and supports approvals, trials, technology transfers and scale up. With the right mix of standards, Organizations can build trust, reduce costly deviations and move products to patients with confidence.
Speak to an auditor at Pacific Certifications, a fifteen minutes call to scope your certification pathway.
Quick summary
"Pharma and life sciences institutions use ISO certifications to strengthen quality, laboratory reliability, information security and business continuity while aligning with Goods practice. Common picks include ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 13485 for medical device quality systems, ISO 14971 for device risk management, ISO 17025 for testing laboratories, ISO/IEC 27001 for information security, ISO 27701 for privacy and ISO 22301 for continuity. Together they support regulatory readiness, supplier approval, trial integrity and measurable performance through KPIs such as deviation closure time, CAPA cycle time, on time calibration and temperature excursion rate."
Introduction
Bringing safe products to market requires more than good science. It needs repeatable systems for quality, validated methods in laboratories, secure handling of patient and study data, controlled suppliers and a supply chain that can maintain conditions end to end. ISO certifications add a common language and audited proof to these goals. They fit alongside Goods practice guidance and support inspections by providing documented scope, risk management, training and records that show how decisions were made and how issues were resolved. The result is clearer governance, faster partner onboarding, better supplier control and fewer surprises during regulatory reviews.
Why ISO certifications matter in pharma and life sciences?
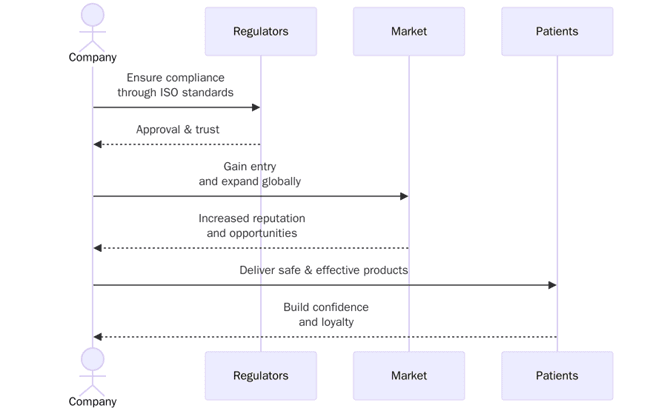
Regulators and partners expect evidence that quality and safety are managed as systems, not one-off activities. Certification gives independent confirmation that controls exist, staff follow them and management reviews outcomes. It also shortens due diligence for licensing, contract manufacturing and research collaborations because buyers can rely on familiar standards. For global supply chains, certification helps align expectations across sponsors, contract research organizations, contract development and manufacturing organizations and distributors.
ISO certifications in pharma and life sciences - quick reference table
Standard | Focus area | Application in pharma & life sciences | Example evidence | Useful KPIs / SLAs |
Quality management | Overall QMS for R&D, manufacturing, distribution | Quality manual, SOPs, audit reports | Deviation closure time, change control lead time | |
Medical device QMS | Devices, diagnostics, combination products | Device master records, design history files | CAPA closure time, complaint closure SLA | |
Risk management | Risk across medical device lifecycle | Risk registers, hazard analyses | Residual risk rate, risk review cadence | |
Laboratory competence | QC, bioanalytical and stability testing | Method validation records, proficiency test results | OOS rate, on time calibration | |
Information security | Clinical data, patient records, IP protection | Access reviews, incident logs, ISMS policies | Incident response time, access review SLA | |
Privacy management | Privacy for clinical and patient data | Consent logs, DSAR responses, privacy notices | DSAR turnaround time, consent withdrawal time | |
Business continuity | Manufacturing sites, labs, distribution continuity | BCPs, test reports, recovery plans | Recovery time objective, recall drill time |
What are the requirements for ISO certification in pharma and life sciences?
To succeed with ISO programs, companies should set clear scope, manage risk and keep reliable evidence. Key requirements include:
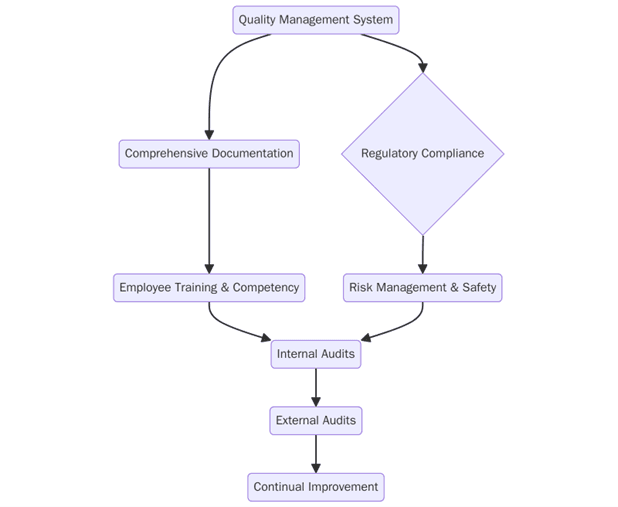
- Define scope and organizational boundaries for research, manufacturing, laboratories and distribution
- Publish policies for quality, risk management, data integrity and security with role clarity
- Conduct risk assessments covering product safety, data integrity, cold chain and supplier reliability
- Document processes for change control, deviation handling, CAPA, training, batch release and validation
- Provide evidence records such as batch records, audit trails, calibration and maintenance logs, stability data and chain of custody
- Train staff and qualified persons with role-based curricula and recertification schedules
- Implement operational controls for cleanroom practice, environmental monitoring, data access and temperature control
- Carry out internal audits and supplier audits with action tracking
How to prepare for ISO certification in pharma and life sciences?
Good preparation brings Goods practice practices and ISO methods into one set of records and controls. Steps that help:
1. Run a gap analysis against the chosen ISO standard and map overlaps with Goods practice procedures
2. Refresh policies and SOPs for data integrity, records, validation and supplier management
3. Train teams on roles for change control, deviations, CAPA and audit readiness
4. Build an evidence index for batches, methods, calibrations, validations and computerized systems
5. Implement controls such as access reviews, environmental and temperature monitoring and electronic signature checks
6. Pilot internal audits on a site or product line and close findings before the external audit
7. Define KPIs and SLAs such as deviation, CAPA, supplier qualification turnaround, instrument calibration on time rate, temperature excursion response time and complaint closure time
Certification audit
Stage 1 audit: Reviews scope, policies, risk assessments, validation approach, laboratory controls and documented records.
Stage 2 audit: Evaluates implementation in manufacturing, QA, QC, R&D, clinical and pharmacovigilance operations, including supplier and cold chain controls.
Nonconformities: Must be corrected with documented proof before approval.
Management review: Confirms leadership oversight, resource allocation and action follow through.
Final certification: Awarded once compliance gaps are resolved.
Surveillance audits: Conducted annually to verify ongoing effectiveness.
Recertification audits: Required every three years to maintain certification.
What are the benefits of ISO certification in pharma and life sciences?
ISO programs support inspection readiness, reduce rework and improve partner confidence. Institutions can link outcomes to KPIs for clear reporting. The main benefits include:
- Stronger quality culture with clear roles and records across sites and partners
- Better laboratory reliability through validated methods and competent staff
- Higher data integrity through access control, audit trails and review cycles
- Reduced supply risk via qualified suppliers, clear SLAs and ongoing monitoring
- Fewer deviations and faster closure through disciplined CAPA and trending
- Improved continuity and recall readiness through tested plans and drills
- Easier market access and partner onboarding with recognized certifications
In recent years, sponsors and regulators have raised expectations on data integrity, supplier resilience and digital systems validation. Organizations are aligning ISO 9001 and ISO 17025 with computerized system validation and data lifecycle controls, while cloud hosted systems are brought under ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO 27701 to protect study data and patient privacy. Temperature controlled logistics now feature SLA terms for excursion response and data availability, with dashboards tracking excursion counts, response time and loss rates.
Contact us
Pacific Certifications provides accredited ISO certification services for pharma and life sciences institutions worldwide. Our audits help align quality, laboratory, security and continuity programs with clear evidence and measurable outcomes.
Request your ISO audit plan and fee estimate, we will help you map Stage 1 and Stage 2 timelines and evidence requirements for your institution. Contact us at [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs

