ISO 13485 + FDA QSR: Building a Harmonized Quality System

In the world of regulated manufacturing of pharmaceuticals and medical devices, product safety, efficacy and quality are paramount. ISO 13485 and FDA QSR (Quality System Regulations) are two important frameworks with requirements that impact product safety, efficacy and quality.
If you are a manufacturer and can build a harmonized quality management system (QMS) to ISO 13485 and FDA QSR, then your responsibility to ensure a product's compliance globally, operating smoothly and product safety is improved. This article will explain how organizations are capable of harmonising these frameworks and will provide considerations for areas of risk management, biological evaluation and integration alongside other standards e.g. ISO 9001.
For assistance, contact us at [email protected]
Introduction
The pharmaceutical and medical device industries are highly regulated to ensure their products are safe and success full. Although ISO 13485 provides a global standard for quality management systems, FDA QSR is regulatory specific for medical device regulation in the United States. While both standards aim for similar objectives - product safety, product quality, and regulatory compliance - the standards vary in their requirements and expectations.
To ensure adherence to ISO 13485 as well as FDA QSR, organizations should align ISO 13485 with FDA QSR to operate the same processes and documentation to support both international and U.S. regulatory requirements and to provide a smooth process for managing quality. An organization that specializes in medical devices to be successful across multiple markets from the U.S. to Europe and beyond will need a harmonized quality management system.
ISO 13485 vs EU MDR: Compliance Checklist
The EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) sets forth stringent requirements for medical device manufacturers within the European Union. Below is a comparison of ISO 13485 and EU MDR, helping manufacturers understand the similarities and differences between the two frameworks.
Risk Management Under ISO 14971 for Pharma Combination Products
ISO 14971 is a key standard for risk management in medical devices, and it also applies to pharma combination products—those that integrate pharmaceuticals with medical devices. Success full risk management is essential for ensuring the safety and functionality of these combination products, which may include drug-delivery devices, inhalers and diagnostic equipment.
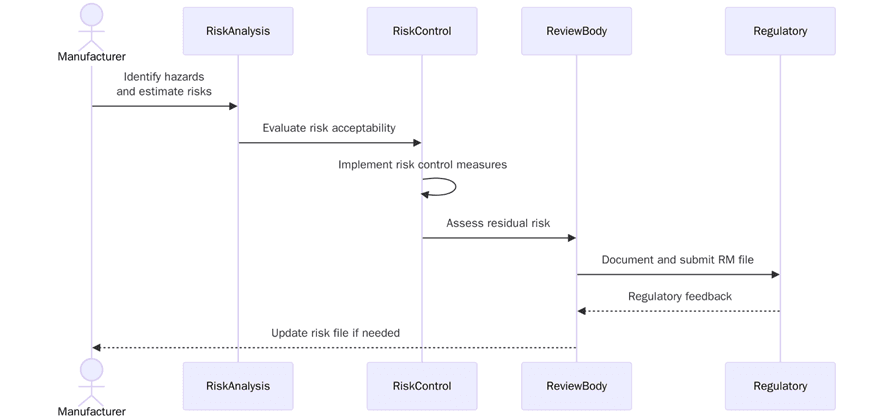
1. Recognizing possible risks related to the device and the pharmaceutical components. This can include biological risks, device failure, or risks associated with exposure to chemicals.
2. Assessing the likelihood and severity (harm) of each risk, and determining if it is acceptable.
3. Identifying measures to mitigate or eliminate the identified risks - this can include design changes, better labelling or improved safety gadgets.
4. Monitoring the products' performance after it has been released to capture any new risks or problems that might emerge, and respond to the issues quickly.
For assistance, contact us at [email protected]
ISO 10993 Biological Evaluation: What SMEs Miss?
ISO 10993 provides the necessary guidelines for the biological evaluation of medical devices. The standard is critical in ensuring that the materials used in devices do not pose a risk to patient health. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), understanding the full scope of ISO 10993 is essential to ensuring product safety and regulatory compliance.
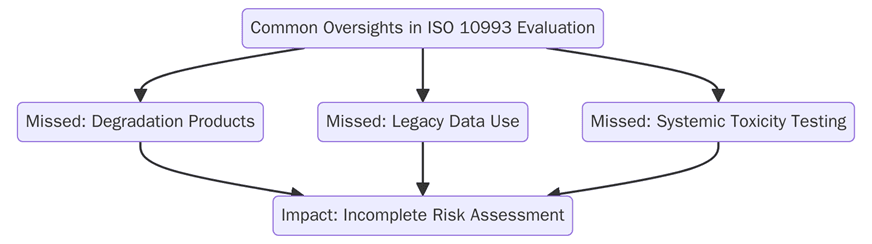
Common mistakes that SMEs make when applying ISO 10993 include:
• Biological risk assessments of all materials in contact with the body, including packaging materials, are often not performed by SMEs.
• When SMEs fail to conduct biological assessments (cytotoxicity, irritation, sensitization, etc.) necessary for required biological testing they become noncompliant to regulatory frameworks and will not achieve the ultimate goal of bringing safe products to market.
• SMEs overlook the evaluation of biocompatibility for all materials, and not just materials in direct contact with the body, can introduce unknown risks.
• Regional variation exists in biological testing and evaluation requirements which may bubble up when SMEs make design decisions for global markets.
21 CFR Part 820 Alignment with ISO 13485:2024 Revision
21 CFR Part 820 provides the FDA Quality System Regulation (QSR) for medical device manufacturers in the United States, and ISO 13485:2024 is the international standard for medical device quality management. For manufacturers to understand and integrate these two frameworks is critical to be able to sell to customers in both U.S. and international markets. Both the frameworks require document control in order to ensure a quality management system or process is adequately documented and the documents are tracked through any changes to the intended audience. Both also have a requirement for a corrective and preventative action system required of manufacturers to address any nonconformities and potentially have better quality or prevent recurrences
Audit Readiness Toolkit for Medical Device Startups
For medical device entrepreneurs, maintaining audit readiness is key to understanding that their quality systems meet the regulators and the quality management systems be able to pass external inspection audits. An Audit Readiness Toolkit can provide help to the entrepreneur for preparing for and managing audits from regulators, certification organizations or external clients.
Best practice, ready-to-use templates for developing and managing evidence of quality systems documentation, such as SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures), work instructions and records of product testing and validation. A overreaching checklist to include every required element of ISO 13485, FDA QSR and others for a complete set during audits, to ensure nothing is left out of the audits. Training in audit procedures for employees, so they will be prepared to answer questions and supply paperwork when required in audits.
Contact Us
Pacific Certifications can assist your organization in navigating the ISO 13485 certification process and aligning it with FDA QSR and other relevant regulatory frameworks. Our team of experts will guide you through building a harmonized quality system that ensures product safety and regulatory compliance.
If you need support with ISO 13485 and FDA QSR, contact us at [email protected].
Read More at: Blogs by Pacific Certifications

