What Are the 7 Elements of ISO 45001? Process Details Explained

Introduction
Creating a safe and healthy workplace is not just a compliance requirement, it’s a moral and operational responsibility. Across industries, organizations face increasing pressure to reduce workplace risks, improve safety performance and protect employees from injury or ill health. ISO 45001:2018, the international standard for Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS), provides a structured framework for achieving exactly that.
Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO 45001 replaces OHSAS 18001 and focuses on integrating safety into business processes through leadership commitment, worker participation and continuous improvement. Whether in construction, manufacturing, logistics, or services, ISO 45001 helps organizations establish processes that identify hazards, assess risks and create a culture of prevention.
Book a 20-minute call with an auditor at Pacific Certifications to explore how ISO 45001 certification can strengthen your organization’s workplace safety culture.
Quick summary
ISO 45001 provides organizations with a systematic approach to manage occupational health and safety risks, prevent incidents and meet legal requirements. Its framework follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle and consists of seven key elements that guide institutions from identifying hazards to achieving continual improvement. These elements: context, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation and improvement — form the backbone of an effective OHSMS.
Why ISO 45001 matters for organizations?
Every organization, regardless of size or sector, faces health and safety risks. Implementing ISO 45001 not only minimizes accidents but also improves operational control, employee confidence and legal compliance. It helps institutions move from reactive to preventive management by embedding safety into daily processes. This ensures that risk identification, incident response and safety audits are handled systematically rather than informally.
“ISO 45001 transforms safety management from isolated procedures into an integrated, organization-wide system that protects people, builds trust and drives consistent performance improvement.”
The 7 elements of ISO 45001 and their process details
ISO 45001 is organized into seven core clauses (4–10), each designed to ensure that occupational health and safety principles are implemented, monitored and continually improved across all organizational levels.

1. Context of the organization
Understanding the internal and external context is the foundation of any management system. Organizations must determine the issues that can affect their ability to achieve occupational health and safety objectives. This involves identifying legal, cultural, economic and operational factors as well as defining the scope of the OHSMS.
The process includes evaluating internal processes, workforce demographics and external factors such as supply chain complexity or regulatory expectations. By defining this scope clearly, the organization sets boundaries for what the OHSMS covers and ensures that all significant risks are addressed.
2. Leadership and worker participation
Leadership plays a vital role in creating a safety-focused culture. ISO 45001 requires top management to establish a clear health and safety policy, assign responsibilities and ensure that workers are actively involved in safety initiatives.
Worker participation is not optional, employees must be consulted during risk assessments, policy reviews and improvement activities. This engagement creates shared accountability and enhances the system’s effectiveness. Strong leadership combined with active worker participation ensures that safety objectives align with broader organizational goals.
3. Planning
Planning under ISO 45001 focuses on identifying risks and opportunities and determining how to address them. Organizations must conduct hazard identification, risk assessment and legal compliance evaluations before setting safety objectives.
This process includes using the hierarchy of controls to eliminate or mitigate risks, developing prevention plans and aligning goals with measurable targets such as incident-rate reduction or training completion. Effective planning ensures that safety is not an afterthought but a proactive, data-driven process.
4. Support
Support covers the resources, competence and documentation required to sustain the system. It includes ensuring employees are trained, competent and aware of their safety responsibilities. Proper communication channels must be established to share safety information internally and externally.
Document control is also a key part of this clause. Organizations must maintain and manage safety manuals, procedures and performance records in a controlled environment. Without adequate support, even the most well-designed OHSMS cannot function effectively.
5. Operation
This clause represents the practical implementation of occupational health and safety controls. It focuses on operational planning, control of outsourced activities, procurement safety and emergency preparedness. Organizations must develop documented procedures for all high-risk activities, implement change-management processes and ensure that contractors follow the same safety standards.
Emergency response planning is also required - institutions must anticipate possible crises such as fire, chemical spills, or equipment failure and prepare response strategies through drills and simulations.
6. Performance evaluation
Once the system is implemented, performance must be measured and evaluated. This includes monitoring incidents, near misses, audit findings and key performance indicators (KPIs) such as injury frequency and severity rates.
Organizations must conduct internal audits to verify whether the OHSMS meets both internal and external requirements. Management reviews are then held to analyse performance trends and decide on strategic improvements. Data-driven evaluation ensures continuous alignment between policy intent and real-world outcomes.
7. Improvement
Improvement is the final stage and represents the PDCA cycle’s “Act” phase. It focuses on correcting nonconformities, preventing recurrence and embedding lessons learned into system updates.
Processes here include root-cause analysis for incidents, preventive action tracking and continuous review of policies and objectives. By encouraging a mindset of learning and adaptation, ISO 45001 ensures that occupational health and safety management evolves as workplace risks change.
Certification audit
Stage 1 audit: Evaluates documentation, policies, scope and readiness.
Stage 2 audit: Verifies system implementation, worker participation and safety controls.
Nonconformities: Must be resolved with corrective actions before certification.
Management review: Confirms leadership accountability and oversight.
Final certification: Awarded after successful closure of findings.
Surveillance audits: Conducted annually to maintain certification.
Recertification audits: Occur every three years to renew validity.
What are the benefits of ISO 45001 certification?
Implementing ISO 45001 has a measurable impact on workplace safety, operational control and employee morale. Below are the key benefits:
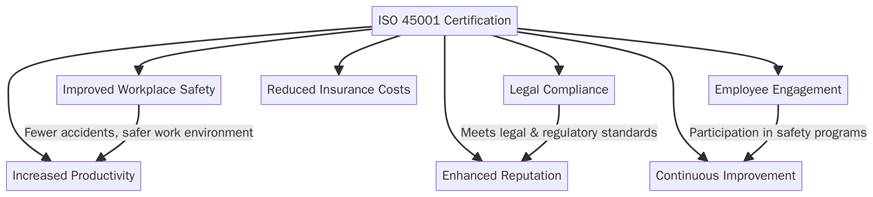
Lower accident and injury rates due to proactive hazard identification and risk management.
Improved compliance with occupational safety legislation and international requirements.
Stronger employee participation and safety culture across all levels.
Reduced absenteeism and downtime caused by workplace incidents.
Better supplier and contractor management through consistent safety controls.
Enhanced organizational reputation and stakeholder confidence.
Easier integration with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 management systems.
Reduced insurance premiums through demonstrated risk control.
Clear KPIs such as incident frequency, audit closure time and training effectiveness.
Long-term resilience through continuous learning and improvement.
Market Trends
Organizations are using technology to improve safety data collection, predictive risk analytics and remote audit capabilities. Cloud-based dashboards, digital permit-to-work systems and AI-driven incident prediction tools are now common in ISO 45001 implementations. Integration of safety with environmental and quality management systems is also increasing as industries seek unified governance models.
By 2030, occupational health and safety will be deeply integrated into sustainability reporting and ESG frameworks. ISO 45001-certified organizations will not only demonstrate safe operations but also transparent reporting of workforce well-being and risk management performance. AI-assisted audits, real-time safety monitoring and predictive compliance tools will further automate system maintenance and improvement.
Training and courses
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs for ISO 45001 to help professionals and organizations build strong occupational health and safety management capabilities:
Lead Auditor Training: Designed for professionals responsible for auditing ISO 45001 systems. It covers audit planning, execution, evidence collection and reporting in line with ISO 19011. Participants learn how to assess risk control measures, management commitment and worker participation.
Lead Implementer Training: Intended for safety officers, HR managers and compliance leaders implementing ISO 45001 within their organization. The course focuses on risk assessment methods, operational control setup, training management and continual improvement tracking.
Contact [email protected] to schedule ISO 45001 training or awareness sessions and strengthen your workplace safety system.
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications provides accredited ISO 45001 certification services to organizations across sectors. Our audits help institutions improve system performance, maintain compliance and build trust with employees, clients and regulators. We focus solely on impartial audit and certification, ensuring transparency and credibility.
Request your ISO 45001 audit plan and fee estimate. We will help you map Stage-1/Stage-2 timelines and evidence requirements for your organization. Contact us at [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Ready to get ISO 45001 certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Author: Alina Ansari
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs

