Understanding ISO 27001 Certification Cost and Key Factors

Introduction
Cyber risk has moved from the server room to the board table. Buyers now ask for proof of control maturity, insurers want evidence before underwriting and regulators expect clear records of how information is protected. ISO/IEC 27001 remains the most recognized way to show that an institution runs an information security management system that is measurable and repeatable. The big question leaders ask is not just “what does it cost?” but “what drives the cost, what value do we get and how do we control it without cutting corners?” This guide explains the cost components, the factors that move them up or down and the choices that help you plan a clean path to certification.
Request a no-obligation audit plan from Pacific Certifications to map scope, audit days and evidence expectations for your ISMS.
Quick summary
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certification costs are driven by scope size, locations, headcount in scope, process and tool maturity, cloud and supplier dependencies and audit time needed to verify controls. Direct costs include the certification audit and annual surveillance. Indirect costs include time for risk assessment, control implementation, records and team training. Institutions control cost by scoping wisely, fixing obvious gaps before audit and keeping evidence clean so audit time stays focused and predictable.
Why ISO 27001 certification matter?
Customers see fewer breaches when suppliers run a live ISMS with clear roles, risk decisions and tracked actions. Certification reduces friction in sales, shortens security questionnaires and supports cyber insurance placement. It also aligns with privacy and sector rules so one set of records can support many requests.
“ISO 27001 converts scattered security tasks into one operating system for risk, giving leaders traceable decisions, measurable controls and audit-ready evidence.”
Key Cost Drivers to Consider
Cost is not a single line item. It is a basket of audit time, people time and targeted improvements. The following areas shape your budget and timeline.
- Scope and boundaries
Products, services, sites, legal entities, cloud accounts and third parties. A tighter scope reduces audit days but must still cover information flows that matter to customers. - Organizational complexity
Number of in-scope employees, locations, time zones, languages and the mix of on-prem and cloud. Multi-site sampling saves time when processes are uniform. - ISMS maturity at the start
Are policies current, risks assessed and controls working. Clean change records, asset lists, access reviews and incident logs reduce time spent during the audit. - Annex A control set
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 groups 93 controls into themes like Organizational, People, Physical and Technological. Your chosen controls and depth of implementation affect preparation effort. - Suppliers and cloud
More third parties mean more due diligence and monitoring evidence. Clear SLAs and SOC or ISO attestations from key providers reduce review effort. - Legal and regulatory bindings
Sector rules, data residency and privacy duties increase depth of testing and record-keeping. - Internal resourcing
If the security, IT and compliance teams are aligned and trained, prep time drops. If not, more time is needed to build evidence. - Audit cycle
Year 1 certification includes Stage 1 and Stage 2. Years 2 and 3 include surveillance. Year 4 is recertification. Planning each year’s evidence keeps costs steady.
ISO 27001 cost components at a glance
Cost area | What it covers | What moves it | How to control it |
Certification audit | Stage 1 readiness review and Stage 2 implementation review | Scope size, sites, evidence quality | Keep scope crisp, align processes, prepare clean records |
Surveillance audits | Annual checks in years 2 and 3 | Changes in scope and risk | Hold steady processes, keep KPIs current |
Preparation effort | Risk assessment, SoA, procedures, records | Starting maturity, tool coverage | Reuse what exists, fix high-impact gaps first |
Tools and controls | MFA, logging, EDR, backup, DLP, monitoring | Current toolset, integration needs | Use what you own, focus on control outcomes |
Training and awareness | ISMS roles, secure use, incident handling | Headcount in scope | Short, role-based modules tied to risks |
Supplier oversight | Due diligence and monitoring | Number and criticality of suppliers | Tier suppliers, require evidence once, store centrally |
What are the requirements for ISO 27001 certification?
Before you list tasks, align the team on what “good” looks like. The ISMS must be scoped, risks must be known and treated and controls must be lived in daily work, not just written down. Below are the key requirements:
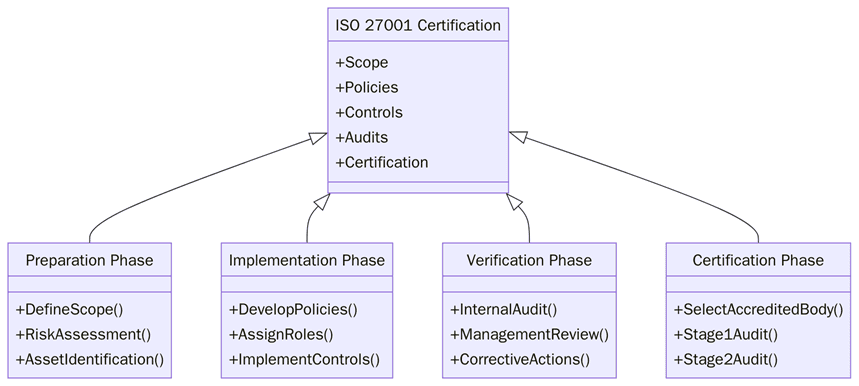
- Define scope and organizational boundaries for the ISMS and key information flows.
- Approve an information security policy and set measurable objectives.
- Perform risk assessment and keep a risk treatment plan with owners and deadlines.
- Build a current Statement of Applicability that maps chosen Annex A controls.
- Maintain core records: asset inventory, access control, change logs, incident logs, supplier records, training logs and internal audit reports.
- Run internal audits and management reviews on a set cadence with tracked actions.
- Keep legal and contractual requirements in a register and verify conformance.
- Prove the controls work through samples, monitoring and exceptions handling.
- Correct nonconformities and keep closure evidence.
- Prepare for Stage 1 and Stage 2 with evidence indexed and accessible.
How to prepare for certification?
A short, focused preparation lowers audit time and keeps attention on facts. These steps build order and momentum.
- Run a gap review against ISO/IEC 27001:2022 and note only the actions that change outcomes.
- Tighten scope and data flows. Map cloud accounts, key apps and shared services.
- Finalize the risk register and risk treatment plan with due dates and owners.
- Refresh core procedures: access, change, backup, incident, vendor and logging.
- Complete staff training for in-scope roles with sign-off records.
- Execute an internal audit and close findings with evidence.
- Hold a management review to confirm resources, decisions and objectives.
Certification audit
Stage 1 audit: Document review, scope, risks, SoA and readiness.
Stage 2 audit: Implementation checks across teams, systems and sites.
Nonconformities: Correct with root cause and closure records before approval.
Management review: Confirms leadership oversight, objectives and resources.
Final certification: Issued after successful closure of findings.
Surveillance audits: Annual checks on key processes, KPIs and changes.
Recertification audits: Every three years to confirm the ISMS still works.
What are the benefits of ISO 27001 certification?
Security programs hold value when they are visible, repeatable and backed by records. Certification helps sales, insurer due diligence and regulator questions while keeping day-to-day discipline on track. Below are the key benefits:
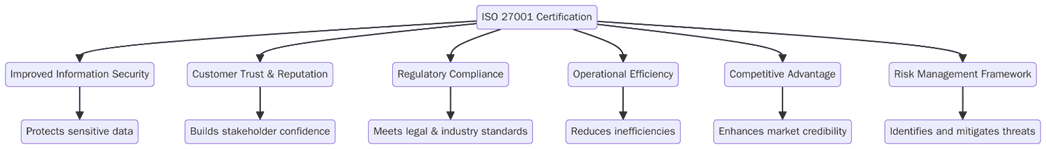
- Shorter vendor security reviews and fewer bespoke audits from customers
- Clear, shared language for risk decisions across IT, legal and business teams
- Better incident readiness with playbooks, on-call roles and evidence trails
- Stronger supplier control through risk tiering and service obligations
- Measurable KPIs that leaders can track and fund with confidence
- Easier alignment with privacy, resilience and sector rules
- Lower rework on audits by using one evidence library for many requests
- Clarity for new hires through defined roles and simple procedures
- Improved change control that reduces outages and access drift
- Credible third-party verification for tenders and investor reviews
Market Trends
If your scope is clear, your records are tidy and controls are working, audit days stay lean and focused. Large swings in cost usually come from unclear boundaries, missing evidence, or frequent last-minute scope changes. Think of cost in two layers: a fixed audit effort based on scope and a variable preparation effort based on how ready you are on day one. Managing both is within your control.
Institutions now blend ISO 27001 with cloud control sets so one dashboard covers MFA, logging, backup and endpoint health. Supplier risk takes a larger share of effort as more work moves to SaaS and managed services. Buyers ask for metrics, not slogans, so teams publish monthly KPIs on access reviews, incident handling and change results. Remote and hybrid audits are common when evidence is digital and sampling is planned.
By 2030, certification will rely more on continuous evidence streams. Logs, access records and change data will support near real-time assurance rather than a once-a-year snapshot. Institutions that invest now in clean inventories, stable processes and role-based training will hold steady cost across the cycle and answer buyer questions in days, not weeks.
Training and courses
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs for ISO/IEC 27001 to build practical capability across teams.
- Lead Auditor Training: Audit planning, sampling, evidence testing, nonconformity grading and reporting aligned with ISO 19011.
- Lead Implementer Training: Scope setting, risk methods, Annex A control mapping, supplier oversight, KPI design and evidence libraries.
Contact [email protected] to schedule ISO 27001 awareness or role-based courses for your teams.
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications provides ISO/IEC 27001 certification and audit services for single sites and multi-site portfolios. We review scope, risks, controls and evidence with clear sampling and predictable timelines. Our assessments are independent. We do not consult. After a successful audit, we issue Certificates of Conformity that your customers and stakeholders can rely on.
Request your ISO 27001 audit plan and surveillance schedule at [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Ready to get ISO 27001 certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Author: Alina Ansari
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs

