ISO Certifications in Zambia, Popular Standards Requirements and Benefits

Introduction
Zambia’s economy is anchored by copper and cobalt mining, mineral processing, agriculture and food chains, hydropower and utilities, construction and engineering, logistics along the North–South Corridor, healthcare and a growing ICT/fintech base around Lusaka, Ndola and the Copperbelt. ISO certification helps Zambian organizations prove stable quality, safer worksites, environmental stewardship, secure information and resilient operations—signals that lenders, export buyers and public procurers accept across SADC, COMESA and global markets.
By adopting standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health & Safety), companies in Zambia can improve efficiency, reduce waste and earn trust from partners and regulators. For growing sectors like ICT, construction and agriculture, ISO certification has become a practical step toward attracting international clients and competing confidently in global markets.
Start your ISO certification journey in Zambia with Pacific Certifications. Email [email protected] for scope, timelines and a clear quote.
Economic Context & Industry Overview
Mining and mineral-processing drive forex earnings, while power generation (including hydropower), construction, transport/logistics and agriculture/food processing support domestic demand and regional trade. Large projects and cross-border supply chains increasingly require documented management systems that control quality, safety, environment and information, with auditable evidence for vendor portals and due-diligence reviews.
Why ISO Certifications matter in Zambia?
Zambia’s economy depends mostly on sectors like mining and agriculture, all industries where quality, safety and sustainability directly affect growth. As the country expands its trade within the SADC and COMESA regions, ISO certifications have become a practical way for businesses to show that they operate responsibly and meet international expectations.
Mining and engineering firms with ISO 9001 can prove the consistency of their production and maintenance processes, while food producers with ISO 22000 or HACCP gain access to regional export markets. Similarly, ISO 14001 helps organizations demonstrate responsible environmental management, something increasingly required in large infrastructure and energy projects.
Another reason ISO certifications matter in Zambia is the growing demand from government and donor-funded tenders. Many public contracts, particularly in construction, utilities and agriculture, now specify certification as an eligibility criterion
Over the next five years, more public infrastructure, energy and manufacturing projects are likely to make ISO certification mandatory in supplier selection. With increased awareness, Zambia’s private and public sectors are gradually building a stronger culture of quality, safety and sustainability.
Popular ISO Standards in Zambia (by industry focus)
Industry focus | Commonly requested standards | Why they matter |
Mining, mineral processing, OEM and contractors | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, ISO 50001 | Consistent quality, environmental controls, safer worksites, energy use control |
Power generation, transmission, utilities | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, ISO 22301 | Service reliability, incident prevention, continuity for critical services |
Manufacturing, engineering workshops | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001 | Product consistency, waste reduction, safe operations |
ICT, data centres, fintech | ISO/IEC 27001, ISO 22301, ISO/IEC 20000-1, ISO/IEC 27701 | Information security, service continuity, IT service quality, privacy governance |
Agriculture, food processing, cold chain | ISO 22000, FSSC 22000, ISO 9001 | HACCP discipline, retailer acceptance, traceability from farm to shelf |
Healthcare, labs, diagnostics | ISO 9001, ISO 15189, ISO/IEC 17025 | Patient confidence and valid test results |
Challenges Faced by Zambian Organizations
Despite the growing interest, several challenges continue to slow down widespread certification adoption in Zambia:
- Many small and medium enterprises find it difficult to budget for certification fees, auditor costs and system maintenance.
- Some organizations still see ISO certification as a foreign concept or an unnecessary compliance burden rather than a business improvement tool.
- Internal auditors and quality managers with ISO experience are in short supply, especially outside Lusaka and the Copperbelt.
- Companies often start implementing ISO systems but struggle with documentation, internal audits and corrective actions needed to maintain certification.
- Because of limited in-house expertise, many rely heavily on external consultants, which increases costs and sometimes affects ownership of the system.
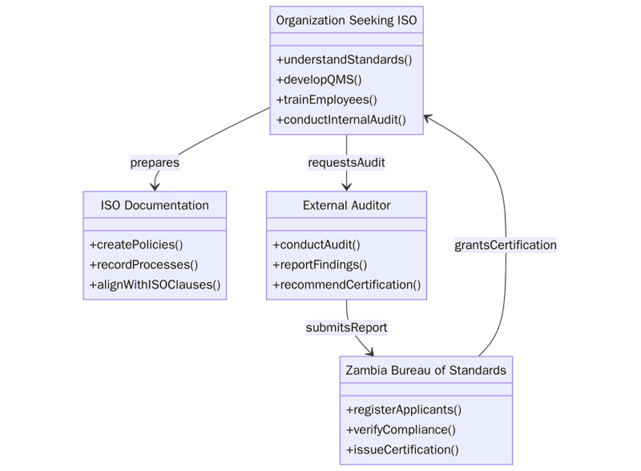
What are the requirements for ISO certifications in Zambia?
Before you begin, anchor the system in Zambia’s operating context. Mining, power, food and ICT carry different risks, so align procedures with real work on the plant floor, at sites, in labs and in data rooms. Keep records that prove the system runs daily, not just at audit time. Below are the key requirements:
- Defined scope aligned to products services and sites
- Documented management system with controlled procedures and records
- Risk assessment and controls aligned to operational realities
- Competence and training records for process owners and key staff
- Completed internal audits with reports NCRs and closures
- Management review with decisions actions and follow-up evidence
- Standard-specific artefacts: HACCP plans (ISO 22000), Statement of Applicability and risk files (ISO 27001), HIRA and PTW logs (ISO 45001), aspect-impact registers (ISO 14001), energy reviews and EPIs (ISO 50001), product realization controls (ISO 29001 where applicable)
- Legal and other needs register with permits inspections calibrations and monitoring data
Tip: Align controls with environmental permits and monitoring, mining/industrial safety rules, food export and cold-chain checks, and data protection expectations in finance/ICT; keep calibration certificates, energy/emissions logs, and supplier test reports ready for sampling.
What are the benefits of ISO certifications in Zambia?
Use certification to win tenders, supply larger customers and stabilize day-to-day work. Track the KPIs your buyers care about so the gains show up in reviews and renewals. Below are the key benefits:
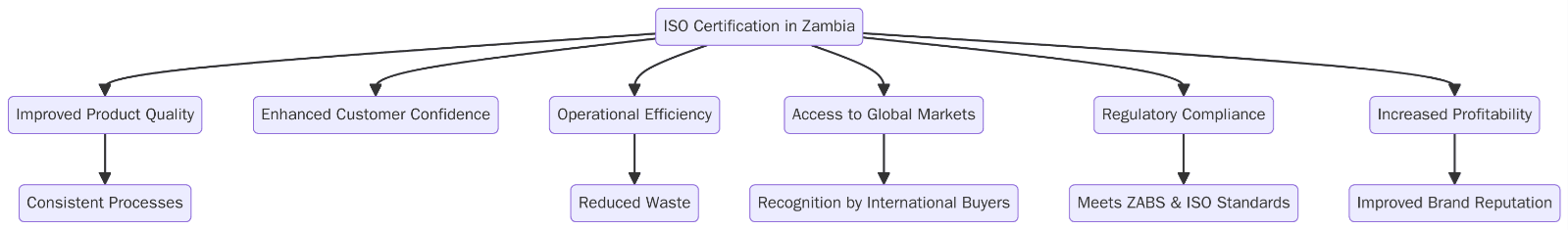
- Credibility with EPCs lenders buyers and regulators
- Lower incidents defects and unplanned downtime across plants and field sites
- Clear roles competence paths and training focus for critical tasks
- Traceable data for due diligence warranty and claims
- Better supplier control through audits KPIs and documented actions
- Measurable gains in energy use waste emissions uptime and yield
- Stronger brand signals for SADC export and cross-border projects
In Zambia, the momentum for ISO certification has picked up in recent years, especially in industries tied to exports and regulation. Major firms in Lusaka, Kitwe and Ndola often highlight ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001 and ISO 27001 among their credentials when bidding for contracts.
One contributing factor is that many public and donor-funded infrastructure or supply tenders now expect and even require ISO certification as a criterion for eligibility. Reports from local ISO consultants indicate that applications and inquiries have risen in sectors like mining, agribusiness, manufacturing, ICT and food processing.
In the mining sector, which is central to Zambia’s export economy companies are under increasing environmental and safety scrutiny. Adopting ISO 14001 (environmental) and ISO 45001 (occupational health & safety) offers a visible way to show compliance, especially when working with international buyers and financiers.
The services sector is catching up too. As telecommunications, fintech and IT firms grow in Zambia, demand for ISO/IEC 27001 (information security) is rising. Digital platforms hold sensitive customer data, so certification gives those firms a credibility boost
At the national level, the Zambia Bureau of Standards (ZABS) plays a key role in standard development and product certification, which gives some institutional backing to ISO efforts.
In summary, Zambia is seeing growing recognition of ISO certification, especially among export-oriented and regulated industries, but broader adoption still faces real obstacles of cost, capacity and awareness.
How to prepare for certification in Zambia?
Preparation starts with an honest view of how work runs today and how evidence is captured. The aim is to make your system auditable without reinventing daily routines. Below are the steps to consider:
- List products services sites headcount and high-risk processes for clear scope
- Map processes end to end to show handoffs records and responsibilities
- Set policy and measurable objectives linked to customer and legal needs
- Assemble evidence packs for production maintenance labs IT and logistics
- Train process owners, keep competence matrices and attendance records current
- Calibrate instruments verify methods and file certificates for quick checks
- Run internal audits that sample high-risk tasks and supplier interfaces
- Hold management review with KPIs audit results complaints legal updates and actions
- Schedule Stage 1 for readiness and Stage 2 for implementation verification, align multi-site sampling to risk
- Blend on-site checks with remote interviews where suitable to reduce travel time
- Keep permits licenses and regulatory reports organized for quick verification
What is the cost of certification in Zambia?
Certification fees are set after scoping and reflect audit-time drivers such as headcount and risk, the number and dispersion of sites (e.g., Lusaka vs. Copperbelt vs. remote operations), chosen standards (single vs. integrated programs like 9001+14001+45001), sector sampling depth (process plants vs. offices), and travel/logistics. Your proposal will clearly itemize Stage 1, Stage 2, and surveillance audit days, note any multi-site sampling efficiencies, and specify on-site versus remote activities so budgets remain transparent and predictable.
For more details, contact [email protected]. .
What is the timeline for certification in Zambia?
Timelines depend on document and record readiness, the speed of closing any Stage-1 gaps, single- vs. multi-site scope, and whether you’re certifying one or several standards in an integrated cycle. Coordinating audit windows around shutdowns, production peaks, harvests, and auditor travel to the Copperbelt or remote sites also affects duration. A well-prepared single site can move from application to decision within one audit cycle, while multi-site or integrated programs typically require additional planning and sampling time.
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications, accredited by ABIS, works with organizations across Zambia to provide independent auditing and certification services for management system, individual training programs and product standards. Whether your business operates in mining, food processing, manufacturing, construction, or ICT, we help you align with internationally recognized ISO standards through a transparent and efficient audit process.
Our approach is straightforward, we focus on understanding your organization’s existing systems, identifying compliance gaps and conducting audits that meet the requirements of the applicable ISO standards. With an experienced network of auditors and technical experts, Pacific Certifications provides certification for a wide range of standards including: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, ISO 22000 / HACCP, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO 50001 etc. Our certificates build credibility in domestic and export markets, improves eligibility for tenders and demonstrates compliance with regional frameworks under SADC and COMESA.
Accredited Training Programs
In addition to certification, Pacific Certifications also offers accredited ISO training programs for professionals and organizations in Zambia, including:
- Lead Auditor Training: for ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, ISO/IEC 27001 and other standards.
- Lead Implementer Training: covering practical implementation techniques for management systems.
These programs are conducted online or onsite, depending on client needs under ISO/IEC 17024 for personnel certification.
To begin the process or request a quotation, contact us at [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Our team will guide you through the audit and certification process and planning stages specific to your operations in Zambia.
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs

