ISO Certifications in Korea, Popular Standards, Requirements and Benefits

Introduction
Korea’s economy runs on high-precision manufacturing, electronics and semiconductors, automotive and shipbuilding, chemicals, healthcare, logistics and fast-scaling digital services across Seoul, Incheon, Gyeonggi, Busan, Ulsan, Daegu and Daejeon. By adopting standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health & Safety), companies in Korea can improve efficiency, reduce waste and earn trust from partners and regulators. For growing sectors like ICT, construction and advanced manufacturing, ISO certification has become a practical step toward attracting international clients and competing confidently in global markets. These programs provide verifiable assurance on quality, safety, environment, information security and continuity that buyers and lenders accept across APAC, Europe and North America.
Contact Pacific Certifications to start your ISO certification application in Korea and receive a documented audit schedule.
Economic Context & Industry Overview
Korea remains one of the world’s most export-oriented industrial economies. Electronics, machinery, automotive, shipbuilding and chemicals anchor manufacturing, while SaaS/cloud, fintech and data-centre services expand the digital footprint. Large buyers and public projects increasingly expect auditable management systems as a baseline for supplier approval, tendering and due diligence.
Why ISO certification matters in Korea?
Export customers and public authorities ask for verifiable systems with clear evidence trails. ISO gives a common assurance language that reduces vendor-approval time, improves safety on complex sites, stabilizes yield in high-precision lines, protects data and uptime for digital platforms and supports HACCP-based traceability for food brands. Certification also organizes the records, policies, KPIs, competence, risk files and corrective actions—so reviews by customers, regulators and lenders move faster and with fewer surprises.
Popular ISO Standards in Korea
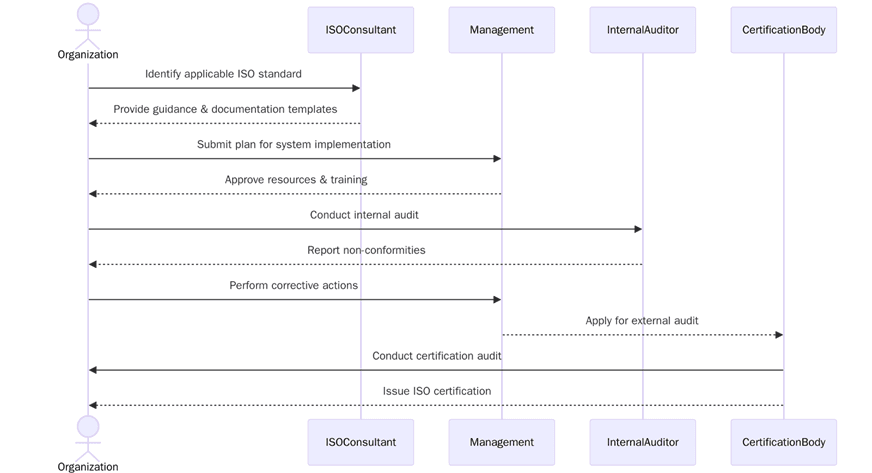
Certification Process in Korea
Preparation starts with an honest view of how work runs today and how evidence is captured. The aim is to make your system auditable without reinventing daily routines. Below are the steps to consider:
List products services sites headcount and high-risk processes for clear scope
Map processes end to end to show handoffs records and responsibilities
Set policy and measurable objectives linked to customer and legal needs
Assemble evidence packs for production maintenance labs IT and logistics
Train process owners keep competence matrices and attendance records current
Calibrate instruments verify methods and file certificates for quick checks
Run internal audits that sample high-risk tasks and supplier interfaces
Hold management review with KPIs audit results complaints legal updates and actions
Schedule Stage 1 for readiness and Stage 2 for implementation verification align multi-site sampling to risk
Blend on-site checks with remote interviews where suitable to reduce travel time
Keep permits licenses and regulatory reports organized for quick verification
What are the requirements of ISO Certifications in Korea?
Build the system around how work actually runs on lines, sites, clinics and data rooms and align with Korean norms so evidence stands up in audits, inspections and buyer reviews; below are the key requirements:
Scope that matches products, services and sites (single or multi-site).
Documented system with controlled procedures and records that match practice.
Risk assessment with controls reflecting real hazards (HACCP, site safety, environmental aspects, privacy/security, energy) and change management.
Competence matrices and training records for process owners and high-risk roles.
Internal audits with reports, nonconformities, root-cause actions and verified closures.
Management review with inputs (KPIs, audits, complaints/incidents, legal updates) and tracked decisions.
Standard-specific artefacts: HACCP & CCP logs (ISO 22000), Statement of Applicability & risk files (ISO/IEC 27001), HIRA & PTW (ISO 45001), aspect-impact registers & objectives (ISO 14001), energy review & EnPIs (ISO 50001).
Legal/other requirements register with permits, inspections, calibrations, monitoring data and supplier compliance evidence.
Tip: Map controls to KOSHA safety guidance, MOE permits and monitoring, MFDS food/HACCP expectations and PIPA privacy duties; keep calibration certificates, utility/energy data, supplier test reports and cold-chain records ready for sampling.
What are the benefits of ISO Certifications in Korea?
Use certification to win vendor status with global OEMs, pass retailer and regulator checks and stabilize operations across shifts and sites; below are the key benefits:
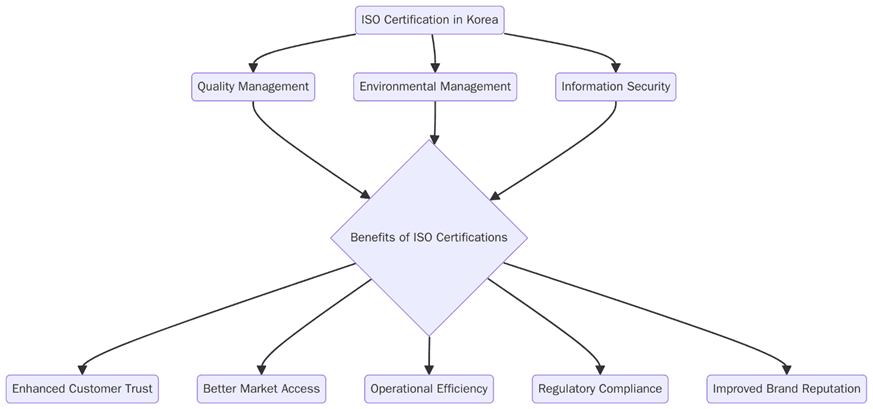
Faster prequalification in buyer portals and public procurement
Fewer incidents, defects and unplanned stoppages on lines and sites
Clear roles and competence paths for critical operations and maintenance
Traceable data for warranty, claims, ESG and due diligence
Better supplier control through audits, KPIs and corrective actions
Measured gains in energy use, waste, emissions, uptime and yield
Stronger brand signals in APAC, EU and US markets
Two medium-term forces will shape ISO demand to 2030. Advanced manufacturing initiatives point to sustained upgrades in quality, safety, environment and energy programs as factories digitize and automate toward 2030 value-add targets, supporting combined adoption of ISO 9001/14001/45001/50001 alongside smart-factory investments. Semiconductor strategy is another driver: national goals to boost chip self-sufficiency by 2030 signal tighter supplier controls and auditability across materials, parts and equipment chains, reinforcing ISO 9001 for yield, ISO 14001/45001 for EHS and ISO 50001 for energy.
Challenges Faced in Korea
Operational, regulatory and evidence readiness issues related to getting certified can cause delays, budget constraints and staffing gaps, incomplete or outdated documentation and records, weak internal audits and corrective actions, supplier-control gaps, multi-site sampling and travel logistics, calibration and permit backlogs and data/privacy mapping for ICT; below are the key challenges:
Budgeting for certification fees, audit time and ongoing system maintenance
Perception of ISO as compliance rather than a performance tool in some teams
Shortage of seasoned internal auditors and process owners in smaller regions
Stalling on document control, internal audits and corrective-action discipline
Multi-site and supplier sampling (e.g., tiered electronics chains) complicating logistics and evidence quality
What is the cost of certification in Korea?
Certification fees are confirmed after scoping and reflect headcount and risk, the number and spread of sites (e.g., Seoul/Gyeonggi/Busan/Ulsan), your standard set (single vs. integrated such as 9001+14001+45001), sector sampling depth (precision lines and cleanrooms vs. offices) and travel/logistics. Your proposal itemizes Stage 1, Stage 2 and surveillance days, clarifies on-site versus remote activities and highlights any multi-site efficiencies so budgets remain transparent and predictable.
For a personalized quote, contact [email protected].
What is the timeline for certification in Korea?
Timelines depend on document and record readiness, the speed of closing any Stage-1 findings, whether you are single- or multi-site and whether the program is single-standard or integrated. Coordinating audit windows around maintenance shutdowns, production ramps, or release cycles—and auditor travel to regional sites—also affects duration. A well-prepared single site can progress from application to decision within one audit cycle, while multi-site or integrated programs typically require additional planning and sampling time.
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications audits and certifies ISO management systems for electronics and semiconductors, automotive and shipbuilding, chemicals and materials, logistics and ports, healthcare and SaaS/cloud across Korea. We work under recognized accreditation with transparent pricing and an experienced local team that understands site realities and buyer expectations. Our certificates are accepted by procurement portals and international customers and we are recognized by ABIS.
Request your ISO audit plan and fee estimate. We will help you map Stage 1 and Stage 2 timelines and evidence requirements for your organization. Contact us at [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Accredited Training Programs
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs in Korea for ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, ISO 22000/FSSC 22000, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO 22301 and ISO/IEC 20000-1.
Lead Auditor Training: for professionals auditing these systems across Korean industries.
Lead Implementer Training: for personnel establishing or improving systems in plants, sites, cold chains, hospitals, utilities and ICT platforms.
These programs are conducted online or onsite, depending on client needs under ISO/IEC 17024 for personnel certification.
To begin the process or request a quotation, contact us at [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Our team will guide you through the audit and certification process and planning stages specific to your operations in Korea.
Author: Ashish
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs

