ISO 31000: Risk Management Framework Explained for Modern Organizations

Introduction
Modern organizations operate in an increasingly volatile environment marked by cybersecurity threats, supply-chain disruptions, climate risks, financial uncertainties, regulatory changes, reputational exposure, and rapidly evolving technology landscapes. Executives, risk leaders, and compliance teams recognize that informal or reactive risk processes are insufficient for enterprise resilience and regulatory credibility.
ISO 31000 provides a structured and internationally accepted risk management framework that helps organizations identify, evaluate, manage, and monitor risks across strategic, operational, financial, digital, environmental, and reputational dimensions. Whether applied in a manufacturing facility, a fintech enterprise, a logistics network, or a government department, ISO 31000 supports evidence-based decision-making, resilience planning, stakeholder confidence, and sustainable business continuity.
True resilience is not measured by avoiding uncertainty, but by mastering it through disciplined and intelligent risk management.
Quick Summary
ISO 31000 establishes principles and guidance for designing, integrating, and maintaining a systematic risk management system across all business functions. Organizations adopt this framework to improve risk visibility, safeguard assets, strengthen governance, enhance decision-making, and maintain regulatory compliance. It offers a scalable methodology for risk identification, evaluation, treatment, and monitoring across any sector.
What is ISO 31000?
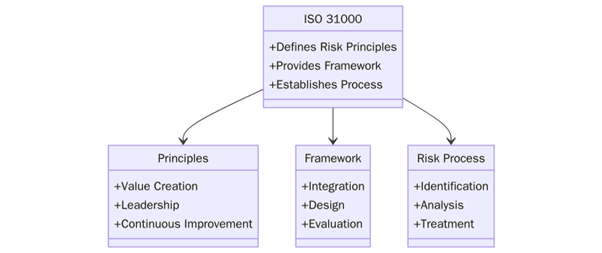
ISO 31000 is an international standard titled "Risk management." Published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), it provides principles, a framework, and a process for managing risk that can be applied to any organization, regardless of size, industry or location.
ISO 31000 is flexible and adaptable, enabling organizations to tailor risk management practices based on their objectives, culture, and external context. Its principles are often used to inform internal audits, corporate governance policies, enterprise risk management (ERM) systems, and integrated management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 27001, ISO 14001).
What is the Purpose of ISO 31000?
The primary purpose of ISO 31000 is to help organizations:
Identify, assess, and manage risks in a systematic and proactive manner
Improve decision-making by understanding risk context and consequences
Foster a risk-aware culture across all levels of the organization
Enhance resilience, agility, and stakeholder confidence
Align risk management strategies with corporate goals and obligations
Rather than simply focusing on risk avoidance, ISO 31000 encourages organizations to also recognize opportunities and make risk-informed strategic decisions.
Need support evaluating your current risk governance? Reach out to [email protected] for audit-readiness assessments.
Scope and Applicability
ISO 31000 applies to all types of organizations, including:
Private companies (SMEs to large enterprises)
Public institutions and governments
Nonprofit organizations
International and regional entities
Project-specific teams or supply chain networks
It is applicable across all industries, such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, energy, education, and technology and can be applied to specific risk types including:
Strategic and reputational risk
Cybersecurity and data privacy
Operational and supply chain risk
Legal, regulatory, and compliance risk
Financial, investment, and credit risk
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks
Key Principles of ISO 31000
ISO 31000 is built upon eight guiding principles that define effective risk management:
Integrated – Risk management must be embedded across all functions and levels.
Structured and comprehensive – A clear and consistent approach enhances results.
Customized – Risk management must align with the organization’s context and objectives.
Inclusive – Stakeholder involvement enhances risk transparency.
Dynamic – Risk management must adapt to changes in the internal and external environment.
Uses best available information – Decision-making should rely on reliable and timely data.
Considers human and cultural factors – Values, perceptions, and capabilities influence risk management.
Facilitates continual improvement – Organizations must review and improve risk processes.
The ISO 31000 Risk Management Framework
The ISO 31000 framework outlines how to integrate risk management into the governance, leadership and reporting systems of an organization. It consists of the following core elements:
Tip: ISO 31000 emphasizes integration — risk management should not be a “compliance box-tick,” but a decision-support tool across strategy and operations.
Risk Management Process (Based on ISO 31000)
The ISO 31000 risk management process includes the following steps:
Communication and Consultation: Engage stakeholders to understand expectations and context.
Establishing the Context: Define the internal and external parameters that influence risk.
Risk Assessment
Risk Identification: What could go wrong?
Risk Analysis: What are the causes, consequences, and likelihood?
Risk Evaluation: Compare against risk criteria to determine significance.
Risk Treatment: Determine how to mitigate, transfer, accept, or avoid the risk.
Monitoring and Review: Track effectiveness of controls and adapt to changes.
Recording and Reporting: Document risk findings, responses, and decisions.
Want to implement a risk register? Pacific Certifications can audit your practices against ISO 31000 process, contact us at [email protected] today!
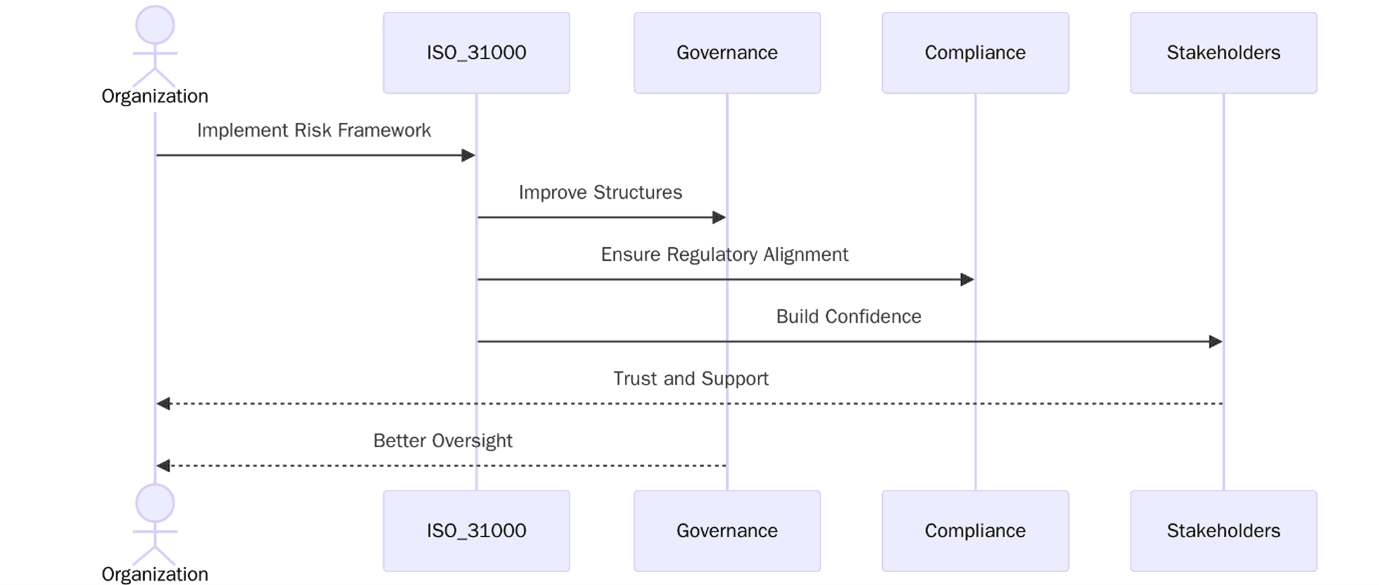
What are the benefits of Implementing ISO 31000?
Enables structured decision-making during crises and uncertainties.
Helps demonstrate due diligence and accountability to stakeholders and authorities.
Transparent risk processes strengthen investor, partner, and public trust.
Risk-informed insights enhance forecasting and scenario analysis.
Enables early detection and mitigation of emerging threats.
In 2025, the implementation of enterprise risk management (ERM) frameworks such as ISO 31000 has become a necessity. Across the globe, organizations are increasingly recognizing that unmanaged risks, whether internal or external, can severely disrupt operational continuity and brand reputation. This is especially evident in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain disruptions and geopolitical uncertainty, all of which have reinforced the need for structured, organization-wide risk governance.
Market Trends
In the United States, regulatory agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) are placing greater emphasis on enterprise risk disclosures, while sectors such as banking, healthcare, insurance, and energy are under growing pressure to prove resilience and accountability. ISO 31000 is being adopted widely as a foundational tool to demonstrate such preparedness and to align risk programs with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting, investor expectations, and third-party risk compliance.
In the European Union, ISO 31000 complements risk-oriented regulations like the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), and it is commonly integrated into compliance programs alongside ISO 27001 for information security and ISO 22301 for business continuity. Countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands have incorporated ISO 31000 into public sector governance and critical infrastructure risk management.
Meanwhile, in rapidly developing economies across Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa, ISO 31000 is increasingly used to professionalize corporate governance, particularly in industries that are expanding rapidly—such as fintech, logistics, aviation, and digital services. In India, UAE, Singapore, and South Africa, governments and regulators are encouraging the private sector to strengthen risk oversight, with ISO 31000 providing a non-prescriptive but globally aligned methodology for scalable adoption.
Multinational corporations and NGOs are also applying ISO 31000 to unify risk management practices across borders, facilitate risk-based decision-making in strategic planning, and promote cultural transformation toward risk awareness at all levels.
Implementation Timeline
Is ISO 31000 Certification Available?
ISO 31000 is a guidance standard, not intended for formal certification. However, many organizations seek third-party audits based on ISO 31000 principles to:
Strengthen governance reporting
Demonstrate internal compliance
Support integrated management systems
Want an external audit or validation of your risk management practices? Pacific Certifications offers structured ISO 31000-based assessments. Contact [email protected].
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
As an accredited certification body, Pacific Certifications offers:
Third-party audits and assessments aligned with ISO 31000 principles
Risk maturity evaluations for strategic alignment
Training programs for ISO 31000 Lead Implementer and Risk Managers
Integration support with other ISO management systems (e.g., 27001, 22301, 9001)
Whether your organization is just beginning to manage risk formally or seeking to refine its risk framework, we help ensure your systems are practical, effective, and globally aligned.
ISO 31000 Training Programs by Pacific Certifications
Pacific Certifications offers internationally recognized training programs that build competence at all levels—from awareness to implementation and auditing. Our training is developed and delivered by experienced auditors and risk professionals to ensure practical, actionable learning. Below are our popular programs:
1. ISO 31000 Awareness Training
This 2 day program introduces participants to:
The principles and structure of ISO 31000
Risk terminology, roles, and responsibilities
Basic risk identification and treatment approaches
Practical examples of applying ISO 31000 in day-to-day decision-making
2. ISO 31000 Lead Implementer Training
This 5-day in-depth course is designed for professionals responsible for designing and embedding risk frameworks. It covers:
Risk governance and the ISO 31000 framework structure
Developing risk registers and treatment plans
Aligning risk with ISO 9001, ISO 27001, or ISO 22301 systems
Engaging leadership and building a risk culture
Creating metrics and KPIs for risk management performance
Certification: Successful participants receive a Lead Implementer Certificate accredited by Pacific Certifications.
3. ISO 31000 Lead Auditor Training
This 5-day intensive course prepares individuals to audit an organization’s risk management framework against ISO 31000 principles. The course includes:
Understanding audit planning and governance
Risk-based audit techniques and checklists
Evaluating leadership, integration, and monitoring practices
Reporting and nonconformity classification
Preparing audit reports for board and regulatory stakeholders
Certification: Participants receive a Lead Auditor Certificate issued by Pacific Certifications.
To enroll a corporate training proposal, contact our team at [email protected]. Customized onsite and remote delivery options are also available globally!
Contact Us
If you need support with ISO 31000 certification, contact us at [email protected].
Author: Ashish
Read More at: Blogs by Pacific Certifications

