Implementing ISO 13485 for Medical Devices and Key Mistakes

Introduction
The medical device industry continues to expand as institutions work to meet global expectations for safety, traceability and product reliability. ISO 13485 has become the central quality requirement for manufacturers, component suppliers, testing facilities, sterilization partners and distributors who want to establish strong control over design, production and post-market performance. As regulatory scrutiny continues to increase and global supply chains become more interconnected, adopting ISO 13485 is shifting from optional to necessary. Institutions that implement the standard successfully gain structured control over operations, reduce defect risks and build credibility with regulators, buyers and healthcare partners.
For many organizations, implementation becomes challenging when the QMS is treated as a documentation exercise rather than an operational system. ISO 13485 demands clarity in design controls, risk management, sterile processing, procurement oversight and complaint handling. When implemented correctly, it creates reliability throughout the device life cycle and sets a strong foundation for compliance with national and international medical device regulations.
If your institution wants a clear understanding of ISO 13485 implementation or wants to review certification readiness, you can request an ISO 13485 audit plan from Pacific Certifications to evaluate scope, timelines and evidence requirements.
Quick summary
ISO 13485 establishes a structured quality management system for medical device organizations, focusing on risk-based decision-making, product traceability, design and development controls, supplier oversight, sterile processing, market feedback handling and documentation consistency. Implementing the standard allows institutions to align their QMS with regulatory expectations and support high-quality, safe medical device production.
Why ISO 13485 matters for medical device institutions?
Institutions manufacturing or supporting medical device supply chains operate in environments where even minor errors can lead to patient harm, delayed approvals, or regulatory intervention. ISO 13485 sets the foundation for maintaining consistency across design, procurement, production, testing, labelling, distribution and post-market oversight. By adopting the standard, organizations can structure processes, synchronize documentation and monitor performance reliably across the entire device lifecycle.
It also supports regulatory alignment by helping institutions demonstrate control over device compliance requirements, risk mitigation actions and complaint handling performance. For buyers and regulators, ISO 13485 certification shows that the QMS follows an internationally accepted medical device framework.
“Institutions that treat ISO 13485 as an operational system, not paperwork, gain stronger control over device safety, performance consistency and regulatory alignment.”
What are the requirements for ISO 13485?
Before implementing ISO 13485, institutions must understand that the system requires consistency in design controls, risk management, supplier oversight and post-market processes. The requirements ensure a traceable and controlled workflow across the entire product lifecycle. Below are the key requirements:
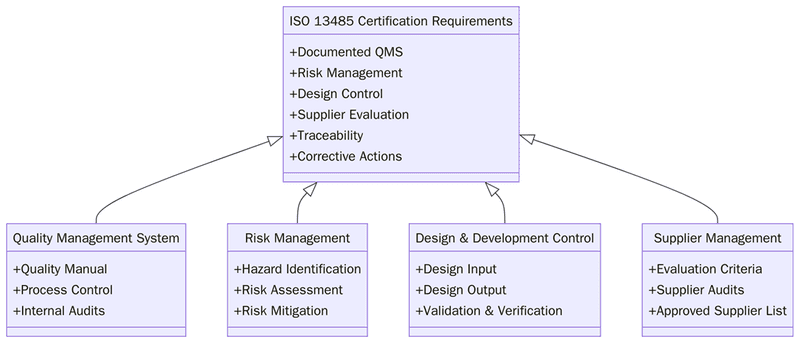
Define the scope of devices, services and processes included in the QMS.
Establish a quality policy and measurable device-related quality objectives.
Maintain documented procedures for design and development controls.
Conduct risk management activities aligned with device hazards and intended use.
Ensure supplier evaluation, monitoring and documented purchasing controls.
Maintain validated production, sterilization and cleaning processes where applicable.
Establish device traceability procedures for components and finished products.
Manage calibration and maintenance of equipment and measuring instruments.
Implement controls for complaint handling, nonconformities and corrective actions.
Conduct internal audits and management reviews at planned intervals.
Tip:Create traceability matrices linking design inputs, risk assessments, verifications and validations to visualize lifecycle control clearly.
How to prepare for ISO 13485 implementation?
Preparing for ISO 13485 involves more than writing policies. Institutions must align processes, responsibilities and quality records with device requirements.
Conduct a structured gap analysis comparing current operations with ISO 13485 clauses.
Prepare a quality manual outlining the structure of your QMS.
Document procedures and work instructions for design, purchasing, manufacturing and testing.
Train personnel on device-specific QMS responsibilities.
Validate manufacturing or cleaning processes that affect device performance.
Strengthen supplier controls using qualification, monitoring and performance records.
Conduct internal audits to confirm readiness for certification.
Certification audit
Stage 1 audit: Review of documentation, design control files, QMS structure and device records.
Stage 2 audit: Verification of implementation across production, testing and traceability.
Nonconformities: Must be resolved with evidence and corrective action records.
Management review: Confirms leadership involvement and QMS effectiveness.
Final certification: Issued once controls meet ISO 13485 requirements.
Surveillance audits: Conducted annually to verify continued control.
Recertification audits: Required every three years to renew compliance.
What are the benefits of ISO 13485?
ISO 13485 provides strong quality assurance for institutions, improves device safety and supports market access. When implemented fully, it builds operational discipline and reduces variability throughout device development and production. Below are the key benefits:
Reduced device defects and improved consistency in production.
Better control over design and development activities.
Stronger regulatory alignment across global medical device markets.
Improved supplier oversight and component reliability.
Enhanced device traceability in case of failures or recalls.
Improved complaint and feedback management.
Better performance visibility through QMS KPIs.
KPIs: defect rate trend, supplier rejection rate, complaint closure time, validation cycle time.
SLAs: supplier response timelines, corrective action closure deadlines, document review cycles.
Better readiness for regulatory inspections and market approval.
Market Trends
Medical device institutions are moving toward stronger risk-based QMS structures aligned with lifecycle performance. Digital quality management tools are improving design documentation, traceability and complaint analytics. Institutions are increasingly using remote audits, cloud-based documentation and predictive performance indicators. Integrated QMS structures combining ISO 13485 with ISO 14971 and ISO 9001 are also becoming more common as device expectations evolve.
In the coming years, institutions will rely heavily on data-driven validation, predictive risk modelling and integrated QMS platforms. Digital traceability systems using RFID and blockchain-based audit trails will support visibility across supply chains. Regulatory systems are expected to align more closely with ISO 13485 structures, making certification a central requirement for market entry, faster approval cycles and international distribution.
Six most common mistakes institutions make during ISO 13485 implementation
Institutions implementing ISO 13485 encounter recurring mistakes that affect compliance and readiness. Addressing these early makes the QMS more reliable.
Treating ISO 13485 as a documentation project instead of an operational system.
Weak risk management with inconsistent linkages to design and process controls.
Incomplete supplier oversight and missing verification records.
Poor traceability across components, batches, or finished devices.
Not validating processes that directly affect device performance.
Insufficient training and unclear role-based responsibilities.
Training and courses
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs for ISO 13485:
Lead Auditor Training: For professionals evaluating device design controls, risk management and traceability.
Lead Auditor Training: For teams establishing or strengthening QMS operations for medical device manufacturing and lifecycle control.
For QMS training tailored to medical device requirements, contact [email protected].
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications provides accredited audit and certification services for ISO 13485. We assess design control files, manufacturing processes, risk management, complaint handling and documentation to verify alignment with the standard. We issue Certificates of Conformity following impartial audits and do not provide consultancy or QMS design services.
To request an audit plan or discuss certification scope, contact [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Read more: Pacific Blogs

