How to Conduct an ISO 27001 Internal Audit?

Introduction
In today’s digital-first world, information security is not just an IT responsibility, it’s an organizational obligation. ISO/IEC 27001 provides a globally recognized framework for managing information security, ensuring confidentiality, integrity and availability of data. However, certification is only one part of the journey. Maintaining it requires consistent internal audits that validate whether the Information Security Management System (ISMS) remains effective, compliant and continuously improving.
An internal audit under ISO 27001 is more than a procedural review; it’s an opportunity to uncover gaps, strengthen controls and confirm that security practices match the organization’s risk appetite.
Schedule an ISO 27001 internal audit preparation session with Pacific Certifications to assess your ISMS readiness and compliance posture.
Quick summary
An ISO 27001 internal audit is a structured, evidence-based evaluation of how well an organization’s ISMS meets the standard’s clauses and Annex A controls. It helps verify whether risk assessments, controls and processes are implemented and maintained effectively. Internal audits are mandatory under Clause 9.2 of ISO/IEC 27001:2022 and are essential for certification, surveillance and continuous improvement.
Why internal audits are vital for ISO 27001?
The internal audit ensures that the ISMS functions as intended and aligns with business, legal and regulatory requirements. It provides management with assurance that security risks are being managed and that any nonconformities are promptly addressed.
Regular internal audits support readiness for external audits, reduce the risk of breaches and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
“An effective internal audit is not about finding faults, it’s about finding opportunities to make your ISMS stronger, smarter and more resilient.”
Table: ISO 27001 Internal Audit Process Overview
What are the requirements for an ISO 27001 internal audit?
Before performing an audit, the organization must define its ISMS scope, controls and objectives clearly. The audit must be systematic, impartial and based on objective evidence. Below are the requirements outlined under Clause 9.2:
Establish an internal audit procedure defining roles, responsibilities and frequency.
Develop an audit schedule covering all processes and controls over a defined cycle.
Define audit criteria aligned with ISO 27001 clauses and Annex A controls.
Appoint competent auditors independent of the area being audited.
Conduct the audit using evidence sampling and interviews.
Record findings, including observations and nonconformities.
Communicate results to management for corrective action.
Monitor the effectiveness of corrective measures.
Maintain records of audit results and follow-ups.
Review the audit process itself for continual improvement.
Tip:Use a risk-based approach: prioritize auditing areas with higher information security risks or past incidents first.
How to prepare for an internal audit?
Preparation ensures that the audit is efficient and provides meaningful insights. Institutions that prepare with up-to-date documentation and evidence reduce audit time and increase accuracy.
Review ISMS documentation including the Information Security Policy, risk register and Statement of Applicability (SoA).
Verify that controls are mapped to identified risks.
Collect and organize evidence such as access control logs, incident reports, training records and supplier reviews.
Check whether previous nonconformities have been closed.
Update internal audit checklists to align with the 2022 version of ISO/IEC 27001.
Brief staff on audit objectives and their expected participation.
Ensure top management involvement in the opening and closing meetings.
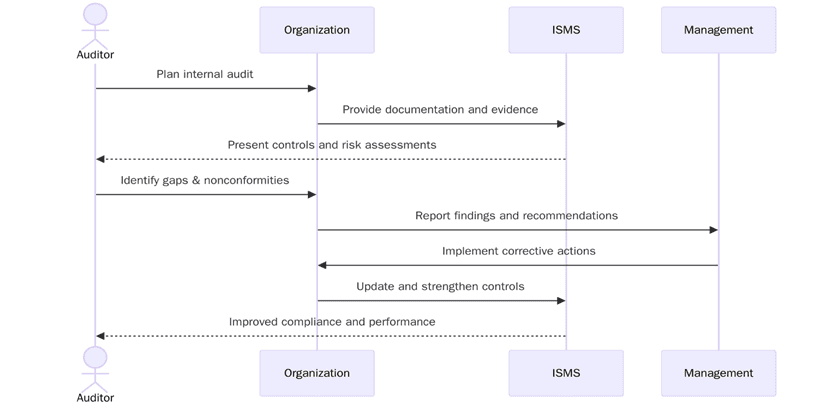
Conducting the audit
A successful internal audit follows a disciplined process that ensures consistency, objectivity and traceability.
Opening meeting: Set expectations, confirm scope and explain methodology.
Document review: Examine ISMS policies, procedures and control records.
Interviews: Speak with process owners and staff to confirm understanding and application of controls.
Evidence sampling: Collect proof of control implementation—such as access logs, encryption settings, supplier SLAs and incident reports.
Evaluation: Compare findings against audit criteria and identify gaps.
Nonconformity classification: Record major and minor nonconformities along with observations.
Closing meeting: Present findings and discuss corrective action plans.
Certification audit flow
Stage 1 audit: Evaluates documentation, policies and audit records to confirm readiness.
Stage 2 audit: Reviews implementation and control effectiveness across the ISMS.
Nonconformities: Require documented corrective actions before certification approval.
Management review: Confirms leadership accountability and ISMS performance.
Surveillance audits: Conducted annually to maintain certification validity.
Recertification audits: Occur every three years to verify ongoing compliance.
What are the benefits of conducting ISO 27001 internal audits?
Internal audits drive continuous improvement and resilience within the organization. They help maintain compliance and enhance the overall security posture. Below are the key benefits:
Early detection of gaps before external audits
Improved risk awareness and control ownership among staff
Reduced likelihood of security incidents and data breaches
Stronger compliance with legal and contractual requirements
Enhanced readiness for customer and regulatory audits
Objective data for management reviews and performance evaluation
Improved documentation accuracy and traceability
Strengthened culture of accountability and continual improvement
KPIs: audit completion rate, nonconformity closure time, repeat finding ratio, risk treatment update frequency
SLAs: response time for corrective action, evidence submission deadline, audit report delivery time
Recent Trends
In recent years, organizations are automating internal audit activities through audit management software integrated with ISMS dashboards. Real-time control monitoring, cloud-based evidence repositories and automated sampling reduce manual effort and increase consistency. AI-assisted audits are also emerging, identifying anomalies in logs and detecting potential control failures automatically.
By 2030, ISO 27001 internal audits will be data-driven and continuous. Instead of periodic manual reviews, organizations will use continuous control monitoring systems that provide live assurance. Machine learning will support risk prediction, highlighting areas that need proactive attention. Internal auditors will act more as data interpreters, focusing on validation, improvement and strategic risk insight rather than checklist verification.
Training and courses
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs for ISO/IEC 27001 internal auditing:
· Lead Auditor Training: Covers planning, conducting, reporting and following up on ISMS audits in line with ISO 19011 guidelines.
· Lead Implementer Training: Designed for professionals responsible for auditing specific departments or processes within their organization.
To register or schedule an internal audit training session, contact [email protected].
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications provides ISO/IEC 27001 certification and audit services, including pre-certification readiness and surveillance audits. Our auditors review ISMS documentation, control implementation and audit records to ensure compliance and continual improvement.
We issue Certificates of Conformity following impartial audits and help organizations maintain long-term certification integrity.
Request your ISO 27001 internal audit checklist and schedule at [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Read more: Pacific Blogs

