Guide to ISO 22000: Food safety Management System

Introduction
Food safety is no longer a secondary consideration, it is a defining factor for trust, brand reputation and long-term sustainability in the global food chain. As food products move through increasingly complex networks of suppliers, manufacturers and distributors, ensuring safety at every step has become a business necessity. ISO 22000 provides a structured and internationally accepted framework for developing, implementing and improving a Food Safety Management System (FSMS) that meets both regulatory and consumer expectations. In 2025, ISO 22000 certification is viewed not only as a compliance measure but also as a strategic advantage, enabling food businesses to compete globally while maintaining transparency and accountability.
Book a food safety readiness discussion with Pacific Certifications to understand how your FSMS aligns with ISO 22000 and what steps you can take toward certification.
Quick summary
ISO 22000 integrates principles of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) and the management framework of ISO 9001. It applies to every organization involved in the food chain, from farmers and feed producers to transporters, retailers and packaging manufacturers. The standard helps institutions identify potential hazards, set preventive measures and maintain traceability. It builds confidence in products, reduces the likelihood of foodborne risks and improves communication throughout the supply chain.
Why ISO 22000 matter for food businesses?
With increasing global trade and consumer awareness, food safety management is now a license to operate rather than an optional investment. ISO 22000 helps organizations align their safety management with international best practices, thereby reducing the risk of recalls, rejections and legal penalties. Certification also ensures that institutions are capable of addressing cross-border regulatory expectations, supplier requirements and buyer audits.
The framework also enhances market access as large retailers, government institutions and international buyers prefer or mandate ISO 22000 certification as part of their sourcing policies.
“ISO 22000 connects every link in the food chain under one system—turning reactive safety control into proactive risk prevention.”
Table: Comparison of ISO 22000, FSSC 22000 and HACCP
What are the requirements for ISO 22000 certification?
Before starting certification, institutions should understand that ISO 22000 is not just about documentation, it’s about embedding food safety culture across every operational layer. The system requires defining the scope, building risk-based processes and ensuring all hazards are identified, monitored and controlled. Below are the key requirements:
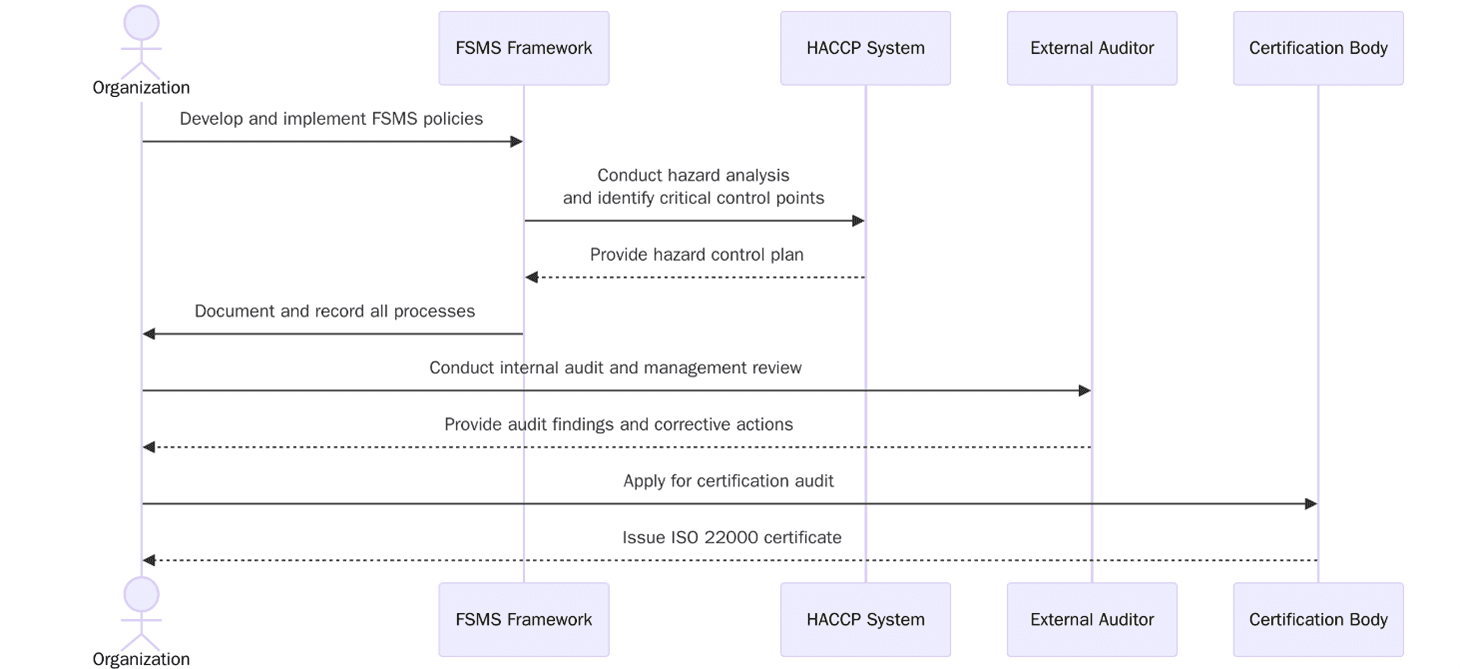
Define the scope of your Food Safety Management System, including all products, services and facilities.
Conduct a hazard analysis to identify biological, chemical and physical risks.
Establish prerequisite programs (PRPs) to maintain hygienic conditions.
Develop and implement HACCP plans that define critical control points and monitoring methods.
Define responsibilities and authority for the food safety team.
Maintain documentation for traceability, corrective actions and verification.
Monitor suppliers and contractors to ensure compliance with food safety criteria.
Develop emergency preparedness and response plans for contamination incidents.
Conduct internal audits and management reviews to track FSMS performance.
Continually improve through data analysis, customer feedback and incident review.
Tip:Use key performance indicators like product defect rate, recall frequency, supplier audit scores and incident closure time to measure system maturity.
How to prepare for ISO 22000 certification?
Preparing for ISO 22000 involves aligning your existing processes with FSMS principles. Institutions that begin with gap analysis and staff training typically experience smoother audits. Below are the steps to prepare:
Conduct a gap analysis against ISO 22000 requirements and HACCP guidelines.
Identify critical suppliers, equipment and processes that affect food safety.
Develop a food safety policy approved by top management.
Map process flows and assigns hazard control responsibilities.
Implement monitoring and corrective action procedures.
Train all staff on hygiene practices and critical control procedures.
Conduct an internal audit and management review before applying for certification.
Certification audit
Stage 1 audit: Review FSMS documentation, hazard analysis and traceability records.
Stage 2 audit: Evaluate implementation across production, storage and distribution areas.
Nonconformities: Must be corrected with documented evidence and root cause analysis.
Management review: Confirms leadership’s role in continuous improvement and resource allocation.
Final certification: Issued after verification of corrective actions and system maturity.
Surveillance audits: Conducted annually to ensure sustained compliance.
Recertification audits: Performed every three years to confirm the FSMS remains effective.
What are the benefits of ISO 22000 certification?
A strong FSMS provides measurable improvements in product safety, customer confidence and operational reliability. Certification also supports business continuity by reducing supply chain risks. Below are the key benefits:
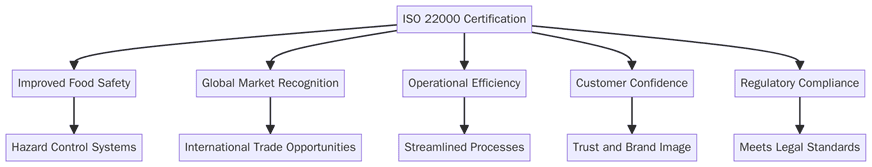
Strengthened global credibility and compliance with international safety standards
Fewer product recalls and lower foodborne illness risks
Improved supplier monitoring and raw material quality control
Consistent product quality and traceability from farm to fork
Enhanced trust from retailers, regulators and consumers
Simplified integration with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 systems
Better team accountability with clear responsibilities and data-driven decisions
Lower costs due to reduced waste, rework and nonconformities
KPIs to monitor progress: recall frequency, audit closure time, customer complaint rates, supplier audit completion percentage
SLAs to maintain consistency: incident response time, quality test turnaround, corrective action closure
Market Trends
Digital traceability and AI-enabled hazard prediction are reshaping food safety management. Institutions are investing in smart sensors, blockchain-based supply tracking and predictive analytics to anticipate contamination risks before they occur. Regulators are increasingly referencing ISO 22000 in compliance frameworks and major retailers in the EU and North America have made ISO 22000 or FSSC 22000 certification mandatory for suppliers.
By 2030, expect ISO 22000 to evolve with integrated sustainability and climate-resilient requirements. Food safety and environmental performance will merge, aligning with carbon footprint reduction goals. Certification bodies will increasingly verify digital records and real-time data instead of traditional paperwork. Institutions that adopt IoT-based monitoring, dynamic risk scoring and cross-border digital compliance platforms will lead the next phase of food system modernization.
Training and courses
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs for ISO 22000 to help food sector professionals strengthen their FSMS understanding:
· Lead Auditor Training: For professionals auditing food safety systems, hazard control plans and PRP effectiveness.
· Lead Implementer Training: For those establishing or improving FSMS within their organization, including supplier management and documentation control.
Contact [email protected] to schedule training or awareness programs for your food safety team.
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications provides ISO 22000 certification and audit services for food producers, processors and supply chain institutions. We perform impartial assessments to verify compliance with ISO 22000 and related standards. Our audits focus on hazard management, control validation, traceability and continual improvement.
We issue Certificates of Conformity, not consultancy services, ensuring credibility and recognition worldwide.
Request your ISO 22000 audit plan or surveillance schedule at [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Ready to get ISO 22000 certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Author: Alina Ansari
Read more: Pacific Blogs

