Biometric Security Guide : Understanding ISO/IEC 30107 Standards
Introduction
Biometrics has rapidly moved from optional authentication to a core part of digital trust. Institutions now rely on facial recognition, fingerprints, iris scans, voice authentication and behavioural biometrics to authenticate users across fintech, healthcare, telecom, public services and high-security environments. As biometric use expands, so do risks related to spoofing, manipulation and presentation attacks. ISO/IEC 30107 provides a structured framework to evaluate the integrity, reliability and security of biometric systems to ensure they cannot be tricked through synthetic media, masks, deepfakes, or fraudulent presentations.
As global digital ecosystems evolve, regulators, auditors and security teams expect stronger evidence that biometric systems are resilient. ISO/IEC 30107 allows organizations to establish trust by validating system resistance to presentation attacks and ensuring biometric data is processed with fairness and accuracy. Institutions using biometric authentication increasingly recognize that compliance with this standard strengthens user confidence and supports long-term governance in identity management.
If you want to understand how biometric security audits work or how ISO/IEC 30107 integrates with your identity governance program, request an audit plan from Pacific Certifications and review how your biometric systems align with global assurance requirements.
Quick summary
ISO/IEC 30107 is the global standard that defines frameworks for detecting, preventing and evaluating presentation attacks against biometric systems. It establishes how biometric verification should respond to fraudulent attempts, how systems must be tested and how assessments should demonstrate trustworthiness. Institutions adopt this standard to validate the reliability of physical and digital identity verification and to reduce risks associated with spoofing or manipulation attempts.
Why biometric standards matter?
Biometric systems are becoming essential in environments where identity verification must be both seamless and trustworthy. With growth in digital services, biometric data is handled across multiple platforms, creating opportunities for misuse if security controls are weak. Presentation attacks such as deepfake facial animations, silicone fingerprints, edited voice recordings, or 3D-printed moulds can cause identity fraud at scale. ISO/IEC 30107 ensures biometric systems undergo strict evaluation to withstand these attempts.
It also provides clear criteria for performance, accuracy, resilience and data protection. Institutions using biometric authentication benefit from structured controls that reduce security incidents, support regulatory needs and build stronger user trust.
“As biometric authentication becomes a default identity layer, ISO/IEC 30107 ensures that institutions can validate system integrity and prevent presentation attacks long before they reach users.”
Overview of ISO/IEC 30107 Framework
What are the requirements for ISO/IEC 30107?
Before implementing the standard, institutions must understand how biometric data behaves, which attack scenarios apply to their systems and which controls must be validated. The requirements build structured assurance across design, testing and monitoring. Below are the key requirements:
Define the scope of biometric systems and identify where presentation attacks may occur.
Establish a biometric security policy that outlines biometric collection, use, testing and retention.
Conduct presentation attack risk assessments for each biometric modality.
Document response processes for detecting attacks and managing failed authentication attempts.
Create testing procedures for biometric PAD mechanisms, covering real and simulated attacks.
Record performance, accuracy rates and failed attempts in structured logs.
Implement data protection controls to secure biometric templates and processing workflows.
Train staff responsible for biometric system monitoring and reporting.
Evaluate presentation attack detection performance using defined metrics.
Review biometric system performance periodically to maintain resilience.
Tip:Build a documented attack library containing past incidents, simulated tests and risk profiles to support future evaluations.
How to prepare for ISO/IEC 30107 assessment?
Institutions preparing for the assessment should ensure their biometric systems follow consistent procedures for analysis, documentation and response. Biometric governance must be integrated with cybersecurity and identity management processes.
Conduct a gap assessment comparing current biometric processes with ISO/IEC 30107 requirements.
Map biometric system architecture and identify PAD dependencies.
Align biometric authentication processes with recognized attack models.
Develop testing protocols using both real and controlled presentation attacks.
Update biometric logs and recordkeeping structures to meet audit evidence needs.
Train teams on managing presentation attacks and handling misuse scenarios.
Conduct internal evaluations before requesting external audits.
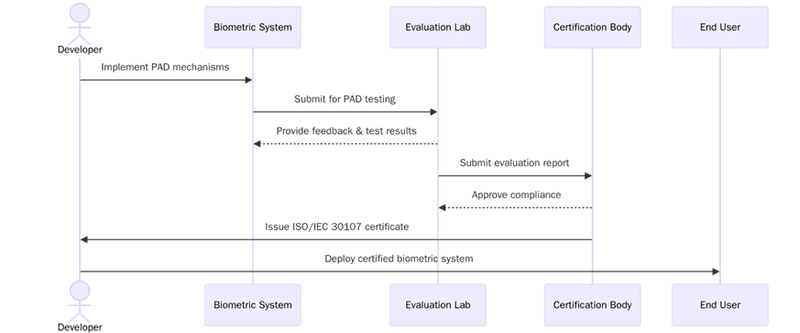
Certification audit
Stage 1 audit: Reviews biometric security documents, PAD framework, logs and biometric policies.
Stage 2 audit: Verifies that presentation attack detection, testing and data controls operate as documented.
Nonconformities: Must be resolved with evidence showing strengthened PAD security.
Management review: Ensures leadership understands biometric risks and testing needs.
Final certification: Issued once PAD controls meet the ISO/IEC 30107 criteria.
Surveillance audits: Conducted annually to ensure ongoing biometric resilience.
Recertification audits: Completed every three years to renew the certificate.
What are the benefits of ISO/IEC 30107?
The benefits of adopting ISO/IEC 30107 extend far beyond regulatory or customer requirements. As biometric authentication becomes central to identity verification, institutions need assurance that these systems cannot be manipulated. The standard helps organizations create strong biometric security structures that protect both users and data. Below are the key benefits:
Increased trust as users gain confidence in secure biometric authentication.
Stronger resilience against spoofing, manipulation and synthetic identity attacks.
Improved biometric performance and consistency across different environments.
Better alignment with national digital identity and data protection regulations.
Reduced risk of fraudulent access across high-security systems.
Better reporting structure with biometric KPIs and incident analysis.
Lower operational disruptions due to biometric system failures.
KPIs: attack detection accuracy, false acceptance rate, biometric uptime.
SLAs: biometric system update cycles, attack response time, audit evidence turnaround.
Stronger internal governance for biometric data management.
Market Trends
Biometric authentication is shifting rapidly toward multimodal security, where systems combine face, voice and behaviour for stronger validation. Presentation attack techniques are evolving quickly, pushing institutions to adopt higher PAD maturity levels and advanced testing frameworks. The rise of deepfake content has increased the need for strict testing protocols and synthetic media detection within PAD assessments. Biometric applications are expanding into remote onboarding, telehealth, finance, border control and digital identity programs, making structured evaluation more important than ever.
In the coming years, biometric systems are expected to integrate AI-driven spoof detection, improved environmental adaptability and stronger protections for biometric templates. Institutions will increasingly require presentation attack testing as part of onboarding new biometric solutions. Regulatory bodies are expected to strengthen biometric compliance expectations, especially in identity verification, payments and public-sector applications. As biometric ecosystems expand, ISO/IEC 30107 will become a baseline requirement for credible and trustworthy digital identity management.
Training and courses
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs for ISO/IEC 30107:
· Lead Auditor Training: Designed for professionals evaluating biometric PAD mechanisms and system performance.
· Lead Implementer Training: Focused on establishing biometric governance, PAD testing frameworks and security controls within institutions.
For customized biometric security training programs, contact [email protected].
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications provides accredited audit and certification services for biometric security and ISO/IEC 30107 compliance. Our audits review biometric controls, PAD mechanisms, system performance and biometric governance to confirm alignment with global standards. We issue Certificates of Conformity following impartial assessments and do not provide consultancy or system development services.
For an audit plan or certification roadmap, contact [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Contact Us
If you need support with ISO/IEC 30107, contact us at [email protected].
Read More at: Blogs by Pacific Certifications

