7 Steps for Handling Waste According to ISO 14001 and Plan-Do-Check-Act Model

Introduction
Waste management has become one of the most pressing challenges for modern organizations. Whether in manufacturing, construction, healthcare, or logistics, effective waste handling not only reduces environmental impact but also improves cost control and compliance with environmental regulations. ISO 14001:2015 provides a structured framework for managing waste systematically through its Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model.
The PDCA cycle helps organizations move from reactive waste control to proactive environmental management. By following these seven steps, institutions can minimize waste generation, optimize resource use and demonstrate strong environmental accountability to clients, regulators and communities.
Speak with an auditor at Pacific Certifications to evaluate how ISO 14001 can help your organization reduce waste, improve sustainability and align with global environmental goals.
Quick summary
The ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management System (EMS) promotes continual improvement by applying the PDCA model Plan (define goals), Do (implement actions), Check (monitor results) and Act (improve performance). Handling waste within this framework ensures compliance, efficiency and measurable environmental results. It transforms waste management from a routine activity into a data-driven process that supports sustainability and profitability.
Why ISO 14001 waste management matters?
Waste handling directly affects an organization’s sustainability profile, operational costs and brand credibility. Poor waste management can lead to regulatory penalties, resource inefficiencies and environmental damage. ISO 14001 enables organizations to approach waste control systematically, from policy creation to performance tracking.
Through a lifecycle perspective, ISO 14001 encourages minimizing waste at the source, managing disposal responsibly and continually improving processes to meet evolving environmental objectives.
“ISO 14001 reframes waste from a by-product into a performance indicator — turning reduction, reuse and recycling into measurable environmental value.”
Step-by-step waste management under ISO 14001’s PDCA model
The Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle provides a continuous improvement loop for managing waste. Below are the seven key steps organizations should follow to align with ISO 14001 requirements.
Step 1: Plan - Identify waste aspects and impacts
Start by identifying the types of waste your organization generates and assessing their environmental impacts. Conduct an environmental aspect analysis to categorize waste as hazardous, non-hazardous, recyclable, or biodegradable. Establish objectives such as reducing landfill disposal or improving recycling rates.
Step 2: Plan - Set environmental objectives and legal obligations
Define measurable waste management goals consistent with your organization’s environmental policy. Consider applicable environmental legislation, permits and customer requirements. ISO 14001 emphasizes aligning objectives with compliance obligations and sustainable resource use.
Step 3: Do - Implement operational controls
Develop and implement documented procedures for handling, storing and disposing of waste. Train employees on segregation practices, labelling and emergency responses for hazardous materials. Collaborate with licensed waste contractors for disposal and recycling activities.
Step 4: Do - Communicate and raise awareness
Communication is central to the ISO 14001 system. Conduct awareness sessions to educate staff about environmental policies and waste management responsibilities. Regular communication builds engagement and ensures waste handling becomes part of the organization’s culture.
Step 5: Check - Monitor and measure waste performance
Once waste management processes are in place, organizations must monitor key performance indicators. Track quantities of waste generated, recycled, reused and sent to disposal. Conduct internal audits to verify compliance with procedures and regulations.
Step 6: Act - Correct nonconformities and improve systems
When deviations or inefficiencies are identified, corrective actions must be taken promptly. Root cause analysis should be applied to identify why nonconformities occurred, whether due to improper segregation, training gaps, or equipment failure. Continuous improvement should then follow..
Step 7: Act - Review and update objectives
Top management should periodically review environmental objectives, including waste management performance, to ensure relevance and alignment with sustainability goals. This reinforces accountability and keeps the EMS responsive to new regulations, technologies and stakeholder expectations.
Tip:Review waste performance quarterly or biannually, integrating it into broader sustainability reporting.
What are the benefits of implementing ISO 14001 waste management?
Implementing ISO 14001 waste management brings both environmental and financial advantages. Below are the key benefits organizations can expect:
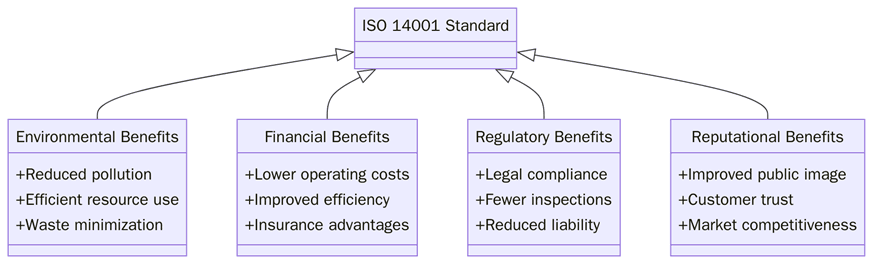
Reduced waste generation and disposal costs.
Improved compliance with local and international environmental laws.
Stronger corporate image through verified environmental responsibility.
Increased material reuse and recycling, lowering raw material expenses.
Data-driven waste management decisions through measurable KPIs.
Enhanced employee engagement through clear environmental roles.
Support for sustainability and ESG reporting frameworks.
Lower carbon footprint and contribution toward circular economy goals.
Recent Trends
In recent years, organizations are moving toward zero-waste certification goals and circular economy initiatives. Many are integrating digital waste-tracking systems, lifecycle assessment (LCA) tools and AI-driven optimization for resource recovery. Governments worldwide are tightening environmental disclosure requirements, making ISO 14001-based systems an essential foundation for compliance and credibility.
By 2030, ISO 14001 is expected to evolve alongside carbon neutrality and net-zero goals. Waste management will shift toward resource efficiency optimization, focusing on redesigning products, reducing single-use materials and converting waste into energy. Certified organizations are projected to achieve 30-40% reduction in total waste disposal and up to 25% cost savings through circular economy practices.
Training and courses
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs for ISO 14001:2015, enabling professionals to build strong environmental management skills:
Lead Auditor Training: For individuals responsible for conducting environmental audits. It includes waste assessment, risk evaluation and compliance verification techniques.
Lead Implementer Training: For environmental managers and officers tasked with developing and maintaining waste management systems. It covers waste segregation procedures, data monitoring and continual improvement strategies.
To schedule training or awareness sessions, contact [email protected].
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications provides accredited ISO 14001 certification and Certificate of Compliance services for waste management systems aligned with the ISO 14001:2015 framework. Our independent audits assess environmental performance, waste handling procedures and continual improvement mechanisms.
For organizations seeking validation of their waste management practices or integration with ISO 14001 environmental systems, Pacific Certifications offers transparent, non-consultative audits that build trust and ensure credibility.
To request your ISO 14001 audit plan and compliance assessment, contact [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Contact Us
If you need support with ISO certification for Waste Handling, contact us at [email protected].
Read More at: Blogs by Pacific Certifications
Author: Alina Ansari

