ISO/IEC 27555: The New Global Standard for Data Deletion Governance

Introduction
Organizations collect huge volumes of customer and employee data across apps, cloud platforms, backups and data lakes. Yet when someone asks for their data to be removed or when a retention period ends, many companies still rely on manual tickets, unclear scripts or partial deletion. This creates risk, wasted storage and gaps between privacy promises and reality.
ISO/IEC 27555 sets out guidance for how personal data should be deleted across systems in a controlled and repeatable way. It connects privacy rules, retention policies, technical deletion methods and evidence of execution so that data is not only stored correctly but also removed when it should be.
If your organization wants to strengthen data deletion practices or review readiness for ISO/IEC 27555-based audits, you can request an audit plan from Pacific Certifications to discuss scope, timelines and required evidence.
Quick summary
ISO/IEC 27555 gives guidance on data deletion governance, with a focus on personal information. It covers deletion concepts and methods, triggers for deletion, roles and responsibilities, documentation, verification and coordination between business, IT and privacy teams. The aim is clear control over when data must be deleted, how deletion is carried out and how the organization proves it.
Why ISO/IEC 27555 matters for data deletion?
Many companies have privacy notices that speak about erasure rights and retention limits, yet their actual data landscape is complex. The same record may appear in transactional systems, logs, data warehouses, test databases and backups. Without a clear deletion framework, data lingers far longer than intended, which increases exposure to misuse, breaches and regulatory action.
ISO/IEC 27555 helps turn data deletion from a case-by-case ticket into part of normal governance. It links legal and business rules with technical methods so that data removal is planned, recorded and verified. For privacy teams, it offers a way to align promises with practice.
What are the requirements for ISO/IEC 27555?
ISO/IEC 27555 is written as guidance, but in practice it behaves like a checklist for data deletion governance. Key expectations include:
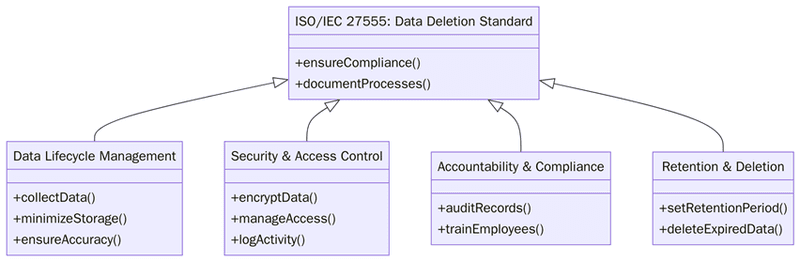
- Define roles and responsibilities for data deletion, including privacy, business owners, IT operations, security and vendors.
- Identify where personal data is stored across systems, services, environments and media, including cloud and on-premise locations.
- Define deletion triggers such as end of retention period, withdrawal of consent, contract end, legal holds being lifted or replacement of data.
- Classify types of deletion such as physical deletion, logical deletion, anonymization and cryptographic deletion, and decide when each method is suitable.
- Develop data deletion procedures for core systems, data warehouses, archives, logs, test environments and backup solutions.
Tip:one of the most useful early steps is to create a “deletion map” that shows key data stores, retention periods, deletion methods and owners in one view.
How to prepare for ISO/IEC 27555 implementation?
Preparing for ISO/IEC 27555 is less about new tools and more about bringing privacy, IT and business teams into one consistent process. Refer to the points below:
- Run a data deletion gap analysis using current practices, system behaviours and policies as inputs, and compare them with the key points above.
- Build or refine your data inventory to show which systems hold personal data, what type of data, who owns it and how long it is kept.
- Align retention rules across legal, privacy and business stakeholders so there is a single authoritative view for each data category.
- Document deletion methods per system, including how data is removed, anonymized or made inaccessible and how long this takes.
- Work with vendors and cloud providers to understand their deletion capabilities and how your organization can request deletion or verify their actions.
Certification audit
Stage 1 audit: Review of data deletion scope, roles and responsibilities, data inventories, retention rules, deletion procedures and high-level integration with privacy governance.
Stage 2 audit: Verification of implementation across selected systems, including deletion records, logs, technical methods, vendor coordination and sample checks on data that should have been deleted.
Nonconformities: Must be corrected with clear root cause analysis, updated controls, improved records and evidence that new practices are in use.
Surveillance audits: Conducted annually to confirm that deletion processes, evidence and coordination remain in place as systems and regulations change.
Recertification audits: Required every three years to review the full framework, including new platforms, data flows and changes in legal or business context.
What are the benefits of ISO/IEC 27555?
ISO/IEC 27555 helps organizations move from informal erasure practices to controlled, auditable data deletion that matches privacy promises. Below are key benefits:
- Better control over personal data lifecycle, from creation to storage and deletion, which reduces unnecessary exposure.
- Clearer link between retention rules and technical behaviour in systems, lowering the chance of hidden data copies.
- More reliable response to data subject rights such as erasure requests, with evidence that data has been handled as promised.
- Easier dialogue with regulators, auditors and business partners, since deletion logic and records are visible and structured.
- Lower storage and backup overhead over time, as data that no longer serves a purpose is removed in a planned way.
Market Trends
Data deletion is moving from an afterthought to a visible part of privacy and cyber planning. Companies are investing in data mapping tools, retention engines and privacy platforms that link customer requests with system-level actions. Many cloud providers now expose APIs for deletion or lifecycle management, which allows closer alignment between policy and practice. At the same time, new storage patterns such as data lakes, event streams and machine learning pipelines create fresh challenges for deletion and anonymization.
Going forward, organizations are likely to treat data deletion as a routine control similar to patching or access reviews. Automation will play a bigger role, but only when supported by clear governance, ownership and rules. ISO/IEC 27555 offers a base for that shift, giving companies a common language and reference when they design, review and certify their deletion practices.
Training and courses
Pacific Certifications support organizations that want to align with ISO/IEC 27555 and strengthen data deletion governance through:
- Lead Auditor Training: for professionals who review data lifecycle controls, deletion records and privacy governance.
- Lead Implementer Training: for teams that design and roll out data deletion frameworks across systems and business units.
For data deletion and privacy training tailored to your environment, contact [email protected].
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications provides accredited audit and certification services for management system standards and can assess organizations that build their data deletion governance around ISO/IEC 27555. Our audits review scope, roles, data inventories, retention rules, deletion procedures, backup handling, vendor coordination, evidence records, internal audits and management review.
To request an audit plan for data deletion governance or discuss ISO/IEC 27555-based certification, contact [email protected] or visit www.pacificcert.com.
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Author: Alina Ansari
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs

